Doppler cooling
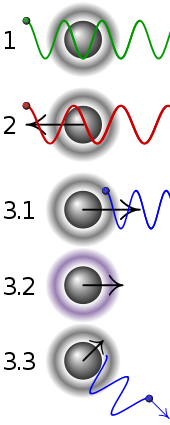
| 1 | A stationary atom sees the laser neither red- nor blue-shifted and does not absorb the photon. |
|---|---|
| 2 | An atom moving away from the laser sees it red-shifted and does not absorb the photon. |
| 3.1 | An atom moving towards the laser sees it blue-shifted and absorbs the photon, slowing the atom. |
| 3.2 | The photon excites the atom, moving an electron to a higher quantum state. |
| 3.3 | The atom re-emits a photon. As its direction is random, there is no net change in momentum over many photons. |
Doppler cooling is a mechanism that can be used to trap and slow the motion of atoms to cool a substance. The term is sometimes used synonymously with laser cooling, though laser cooling includes other techniques.
History
[edit]Doppler cooling was simultaneously proposed by two groups in 1975, the first being David J. Wineland and Hans Georg Dehmelt[1] and the second being Theodor W. Hänsch and Arthur Leonard Schawlow.[2] It was first demonstrated by Wineland, Drullinger, and Walls in 1978[3] and shortly afterwards by Neuhauser, Hohenstatt, Toschek and Dehmelt.[4] One conceptually simple form of Doppler cooling is referred to as optical molasses, since the dissipative optical force resembles the viscous drag on a body moving through molasses. Steven Chu, Claude Cohen-Tannoudji and William D. Phillips were awarded the 1997 Nobel Prize in Physics for their work in laser cooling and atom trapping.[5]
Brief explanation
[edit]Doppler cooling involves light with frequency tuned slightly below an electronic transition in an atom. Because the light is detuned to the "red" (i.e. at lower frequency) of the transition, the atoms will absorb more photons if they move towards the light source, due to the Doppler effect.
Consider the simplest case of 1D motion on the x axis. Let the photon be traveling in the +x direction and the atom in the −x direction. In each absorption event, the atom loses a momentum equal to the momentum of the photon. The atom, which is now in the excited state, emits a photon spontaneously but randomly along +x or −x. Momentum is returned to the atom. If the photon was emitted along +x then there is no net change; however, if the photon was emitted along −x, then the atom is moving more slowly in either −x or +x.
The net result of the absorption and emission process is a reduced speed of the atom, on the condition that its initial speed is larger than the recoil velocity from scattering a single photon. If the absorption and emission are repeated many times, the mean velocity, and therefore the kinetic energy of the atom, will be reduced. Since the temperature of an ensemble of atoms is a measure of the random internal kinetic energy, this is equivalent to cooling the atoms.
The Doppler cooling limit is the minimum temperature achievable with Doppler cooling.
Detailed explanation
[edit]The vast majority of photons that come anywhere near a particular atom are almost[6] completely unaffected by that atom. The atom is almost completely transparent to most frequencies (colors) of photons.
A few photons happen to "resonate" with the atom in a few very narrow bands of frequencies (a single color rather than a mixture like white light). When one of those photons comes close to the atom, the atom typically absorbs that photon (absorption spectrum) for a brief period of time, then emits an identical photon (emission spectrum) in some random, unpredictable direction. (Other sorts of interactions between atoms and photons exist, but are not relevant to this article.)
The popular idea that lasers increase the thermal energy of matter is not the case when examining individual atoms. If a given atom is practically motionless (a "cold" atom), and the frequency of a laser focused upon it can be controlled, most frequencies do not affect the atom—it is invisible at those frequencies. There are only a few points of electromagnetic frequency that have any effect on that atom. At those frequencies, the atom can absorb a photon from the laser, while transitioning to an excited electronic state, and pick up the momentum of that photon. Since the atom now has the photon's momentum, the atom must begin to drift in the direction the photon was traveling. A short time later, the atom will spontaneously emit a photon in a random direction as it relaxes to a lower electronic state. If that photon is emitted in the direction of the original photon, the atom will give up its momentum to the photon and will become motionless again. If the photon is emitted in the opposite direction, the atom will have to provide momentum in that opposite direction, which means the atom will pick up even more momentum in the direction of the original photon (to conserve momentum), with double its original velocity. But usually the photon speeds away in some other direction, giving the atom at least some sideways thrust.
Another way of changing frequencies is to change the positioning of the laser, for example, by using a monochromatic (single-color) laser that has a frequency that is a little below one of the "resonant" frequencies of this atom (at which frequency the laser will not directly affect the atom's state). If the laser were to be positioned so that it was moving towards the observed atoms, then the Doppler effect would raise its frequency. At one specific velocity, the frequency would be precisely correct for said atoms to begin absorbing photons.
Something very similar happens in a laser cooling apparatus, except such devices start with a warm cloud of atoms moving in numerous directions at variable velocity. Starting with a laser frequency well below the resonant frequency, photons from any one laser pass right through the majority of atoms. However, atoms moving rapidly towards a particular laser catch the photons for that laser, slowing those atoms down until they become transparent again. (Atoms rapidly moving away from that laser are transparent to that laser's photons—but they are rapidly moving towards the laser directly opposite it). This utilization of a specific velocity to induce absorption is also seen in Mössbauer spectroscopy.
On a graph of atom velocities (atoms moving rapidly to the right correspond with stationary dots far to the right, atoms moving rapidly to the left correspond with stationary dots far to the left), there is a narrow band on the left edge corresponding to the speed at which those atoms start absorbing photons from the left laser. Atoms in that band are the only ones that interact with the left laser. When a photon from the left laser slams into one of those atoms, it suddenly slows down an amount corresponding to the momentum of that photon (the dot would be redrawn some fixed "quantum" distance further to the right). If the atom releases the photon directly to the right, then the dot is redrawn that same distance to the left, putting it back in the narrow band of interaction. But usually the atom releases the photon in some other random direction, and the dot is redrawn that quantum distance in the opposite direction.
Such an apparatus would be constructed with many lasers, corresponding to many boundary lines that completely surround that cloud of dots.
As the laser frequency is increased, the boundary contracts, pushing all the dots on that graph towards zero velocity, the given definition of "cold".
Limits
[edit]Minimum temperature
[edit]The Doppler temperature is the minimum temperature achievable with Doppler cooling.
When a photon is absorbed by an atom counter-propagating to the light source, its velocity is decreased by momentum conservation. When the absorbed photon is spontaneously emitted by the excited atom, the atom receives a momentum kick in a random direction. The spontaneous emissions are isotropic and therefore these momentum kicks average to zero for the mean velocity. On the other hand, the mean squared velocity, , is not zero in the random process, and thus heat is supplied to the atom.[7] At equilibrium, the heating and cooling rates are equal, which sets a limit on the amount by which the atom can be cooled. As the transitions used for Doppler cooling have broad natural linewidths (measured in radians per second), this sets the lower limit to the temperature of the atoms after cooling to be[8]
where is the Boltzmann constant and is the reduced Planck constant. This is usually much higher than the recoil temperature, which is the temperature associated with the momentum gained from the spontaneous emission of a photon.
The Doppler limit has been verified with a gas of metastable helium.[9]
Sub-Doppler cooling
[edit]Temperatures well below the Doppler limit have been achieved with various laser cooling methods, including Sisyphus cooling, evaporative cooling, and resolved sideband cooling. The theory of Doppler cooling assumes an atom with a simple two level structure, whereas most atomic species which are laser cooled have complicated hyperfine structure. Mechanisms such as Sisyphus cooling due to multiple ground states lead to temperatures lower than the Doppler limit.
Maximum concentration
[edit]The concentration must be minimal to prevent the absorption of the photons into the gas in the form of heat. This absorption happens when two atoms collide with each other while one of them has an excited electron. There is then a possibility of the excited electron dropping back to the ground state with its extra energy liberated in additional kinetic energy to the colliding atoms—which heats the atoms. This works against the cooling process and therefore limits the maximum concentration of gas that can be cooled using this method.
Atomic structure
[edit]Only certain atoms and ions have optical transitions amenable to laser cooling, since it is extremely difficult to generate the amounts of laser power needed at wavelengths much shorter than 300 nm. Furthermore, the more hyperfine structure an atom has, the more ways there are for it to emit a photon from the upper state and not return to its original state, putting it in a dark state and removing it from the cooling process. It is possible to use other lasers to optically pump those atoms back into the excited state and try again, but the more complex the hyperfine structure is, the more (narrow-band, frequency locked) lasers are required. Since frequency-locked lasers are both complex and expensive, atoms which need more than one extra repump laser are rarely cooled; the common rubidium magneto-optical trap, for example, requires one repump laser. This is also the reason why molecules are in general difficult to laser cool: in addition to hyperfine structure, molecules also have rovibronic couplings and so can also decay into excited rotational or vibrational states. However, laser cooling of molecules has been demonstrated, first with SrF molecules,[10] and subsequently with other diatomics such as CaF[11][12] and YO.[13]
Configurations
[edit]Counter-propagating sets of laser beams in all three Cartesian dimensions may be used to cool the three motional degrees of freedom of the atom. Common laser-cooling configurations include optical molasses, the magneto-optical trap, and the Zeeman slower.
Atomic ions, trapped in an ion trap, can be cooled with a single laser beam as long as that beam has a component along all three motional degrees of freedom. This is in contrast to the six beams required to trap neutral atoms. The original laser cooling experiments were performed on ions in ion traps. (In theory, neutral atoms could be cooled with a single beam if they could be trapped in a deep trap, but in practice neutral traps are much shallower than ion traps and a single recoil event can be enough to kick a neutral atom out of the trap.)
Applications
[edit]One use for Doppler cooling is the optical molasses technique. This process itself forms a part of the magneto-optical trap but it can be used independently.
Doppler cooling is also used in spectroscopy and metrology, where cooling allows narrower spectroscopic features. For example, all of the best atomic clock technologies involve Doppler cooling at some point.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^
Wineland, D. J.; Dehmelt, H. (1975). "Proposed 1014
Δν < ν Laser Fluorescence Spectroscopy on Tl+
Mono-Ion Oscillator III" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Physical Society. 20: 637. - ^ Hänsch, T. W.; Shawlow, A. L. (1975). "Cooling of Gases by Laser Radiation". Optics Communications. 13 (1): 68. Bibcode:1975OptCo..13...68H. doi:10.1016/0030-4018(75)90159-5.
- ^ Wineland, D. J.; Drullinger, R. E.; Walls, F. L. (1978). "Radiation-Pressure Cooling of Bound Resonant Absorbers". Physical Review Letters. 40 (25): 1639. Bibcode:1978PhRvL..40.1639W. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.40.1639.
- ^ Neuhauser, W.; Hohenstatt, M.; Toschek, P.; Dehmelt, H. (1978). "Optical-Sideband Cooling of Visible Atom Cloud Confined in Parabolic Well". Physical Review Letters. 41 (4): 233. Bibcode:1978PhRvL..41..233N. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.41.233.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 1997". Nobel Foundation. Archived from the original on 7 October 2008. Retrieved 9 October 2008.
- ^ There are processes, such as Rayleigh and Raman scattering, by which atoms and molecules will scatter non-resonant photons; see, e.g., Hecht, E.; Zajac, A. (1974). Optics. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-02835-5. This type of scattering, however, is normally very weak in comparison to resonant absorption and emission (i.e., fluorescence).
- ^ Lett, P. D.; Phillips, W. D.; Rolston, S. L.; Tanner, C. E.; Watts, R. N.; Westbrook, C. I. (1989). "Optical molasses". Journal of the Optical Society of America B. 6 (11): 2084–2107. Bibcode:1989JOSAB...6.2084L. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.6.002084.
- ^ Letokhov, V. S.; Minogin, V. G.; Pavlik, B. D. (1977). "Cooling and capture of atoms and molecules by a resonant light field". Soviet Physics JETP. 45: 698. Bibcode:1977JETP...45..698L.
- ^ Chang, R.; Hoendervanger, A. L.; Bouton, Q.; Fang, Y.; Klafka, T.; Audo, K.; Aspect, A.; Westbrook, C. I.; Clément, D. (2014). "Three-dimensional laser cooling at the Doppler limit". Physical Review A. 90 (6): 063407. arXiv:1409.2519. Bibcode:2014PhRvA..90f3407C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.90.063407. S2CID 55013080.
- ^ Shuman, E. S.; Barry, J. F.; DeMille, D. (2010). "Laser cooling of a diatomic molecule". Nature. 467 (7317): 820–823. arXiv:1103.6004. Bibcode:2010Natur.467..820S. doi:10.1038/nature09443. PMID 20852614. S2CID 4430586.
- ^ "Laser Cooling CaF". doylegroup.harvard.edu/. Doyle Group, Harvard University. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ Zhelyazkova, V.; Cournol, A.; Wall, T. E.; Matsushima, A.; Hudson, J. J.; Hinds, E. A.; Tarbutt, M. R.; Sauer, B. E. (2014). "Laser cooling and slowing of CaF molecules". Physical Review A. 89 (5): 053416. arXiv:1308.0421. Bibcode:2014PhRvA..89e3416Z. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.89.053416. S2CID 119285667.
- ^ Hummon, M. T.; Yeo, M.; Stuhl, B. K.; Collopy, A. L.; Xia, Y.; Ye, J. (2013). "2D Magneto-Optical Trapping of Diatomic Molecules". Physical Review Letters. 110 (14): 143001. arXiv:1209.4069. Bibcode:2013PhRvL.110n3001H. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.143001. PMID 25166984. S2CID 13718902.
Further reading
[edit]- Foot, C. J. (2005). Atomic Physics. Oxford University Press. pp. 182–213. ISBN 978-0-19-850696-6.
- Metcalf, H. J.; van der Straten, P. (1999). Laser Cooling and Trapping. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-98728-6.
- Phillips, W. D. (1997). "Laser Cooling and Trapping of Atoms" (PDF). Nobel Lecture. Nobel Foundation. pp. 199–237.





