Digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade (/ˈdɪdʒɪtɪˌɡreɪd/)[1] locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin digitus, 'finger', and gradior, 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (phalanges) on the ground, and the rest of its foot lifted. Digitigrades include birds (what many see as bird's knees are actually ankles), cats, dogs, and many other mammals, but not plantigrades (such as humans) or unguligrades (such as horses). Digitigrades generally move more quickly than other animals.
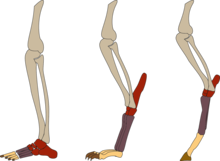
There are structural differences between the limb anatomy of plantigrades, unguligrades, and digitigrades. Digitigrade and unguligrade animals have relatively long carpals and tarsals, and the bones which correspond to the human ankle are thus set much higher in the limb than in a human. In a digitigrade animal, this effectively lengthens the foot, so much so that what are often thought of as a digitigrade animal's "hands" and "feet" correspond to only the human fingers or toes. Digitigrade locomotion is responsible for the distinctive hooked shape of dog legs.
Plantigrade animals, such as humans, normally walk with the soles of their feet on the ground. Unguligrade animals, such as horses and cattle, walk only on the distal-most tips of their digits. Digitigrade animals walk on their distal and intermediate phalanges; more than one segment of the digit makes contact with the ground, either directly (as in birds) or via paw-pads (as in dogs and cats).
Examples
[edit]
- Mesonychidae
- Dinosaurs (digitigrade and semi-digitigrade)
- Suina (semi-digitigrade)
- Hippopotamidae (semi-digitigrade)
- Pakicetus
- Indohyus
- Thylacine
- Felidae
- Hyenas
- Mongooses
- Canidae
- Derived hyaenodonts (range from digitigrade to semidigitigrade: ancestrally plantigrade)
- Elephants (semi-digitigrade)[2]
- Capybaras (semi-digitigrade)
- Trucidocynodon (semi-digitigrade at least in the forelimbs)
- Certain primates (including some monkeys and lemurs)[3]
References
[edit]- ^ "Digitigrade". Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d.
- ^ "APPEARANCE/ MORPHOLOGY: LEGS, SPINE AND TRACKS with literature reports for the Asian Elephant - Elephas maximus (editorial comment)". wildlifeinformation.org. Archived from the original on December 14, 2007.
- ^ https://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/primate-locomotion-105284696/
External links
[edit]- "Yes, the Shin Bone Is Connected to the Ankle Bone". cvm.uiuc.edu. Archived from the original on February 3, 2007.
