Golgi apparatus

| Cell biology | |
|---|---|
| Animal cell diagram | |
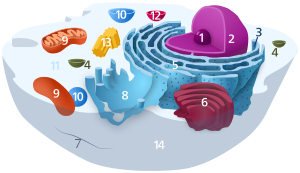 Components of a typical animal cell:
|
The Golgi apparatus (/ˈɡɒldʒi/), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells.[1] Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus was identified in 1898 by the Italian biologist and pathologist Camillo Golgi.[2] The organelle was later named after him in the 1910s.[2]
Discovery
Because of its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system.[3][2] After first observing it under his microscope, he termed the structure as apparato reticolare interno ("internal reticular apparatus"). Some doubted the discovery at first, arguing that the appearance of the structure was merely an optical illusion created by Golgi’s observation technique. With the development of modern microscopes in the twentieth century, the discovery was confirmed.[4] Early references to the Golgi apparatus referred to it by various names, including the Golgi–Holmgren apparatus, Golgi–Holmgren ducts, and Golgi–Kopsch apparatus.[2] The term Golgi apparatus was used in 1910 and first appeared in scientific literature in 1913, while "Golgi complex" was introduced in 1956.[2]
Subcellular localization
The subcellular localization of the Golgi apparatus varies among eukaryotes. In mammals, a single Golgi apparatus is usually located near the cell nucleus, close to the centrosome. Tubular connections are responsible for linking the stacks together. Localization and tubular connections of the Golgi apparatus are dependent on microtubules. In experiments it is seen that as microtubules are depolymerized the Golgi apparatuses lose mutual connections and become individual stacks throughout the cytoplasm.[5] In yeast, multiple Golgi apparatuses are scattered throughout the cytoplasm (as observed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae). In plants, Golgi stacks are not concentrated at the centrosomal region and do not form Golgi ribbons.[6] Organization of the plant Golgi depends on actin cables and not microtubules.[6] The common feature among Golgi is that they are adjacent to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exit sites.[7]
Structure

In most eukaryotes, the Golgi apparatus is made up of a series of compartments and is a collection of fused, flattened membrane-enclosed disks known as cisternae (singular: cisterna, also called "dictyosomes"), originating from vesicular clusters that bud off the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). A mammalian cell typically contains 40 to 100 stacks of cisternae.[8] Between four and eight cisternae are usually present in a stack; however, in some protists as many as sixty cisternae have been observed.[4] This collection of cisternae is broken down into cis, medial, and trans compartments, making up two main networks: the cis Golgi network (CGN) and the trans Golgi network (TGN). The CGN is the first cisternal structure, and the TGN is the final, from which proteins are packaged into vesicles destined to lysosomes, secretory vesicles, or the cell surface. The TGN is usually positioned adjacent to the stack, but can also be separate from it. The TGN may act as an early endosome in yeast and plants.[6][9]
There are structural and organizational differences in the Golgi apparatus among eukaryotes. In some yeasts, Golgi stacking is not observed. Pichia pastoris does have stacked Golgi, while Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not.[6] In plants, the individual stacks of the Golgi apparatus seem to operate independently.[6]
The Golgi apparatus tends to be larger and more numerous in cells that synthesize and secrete large amounts of substances; for example, the antibody-secreting plasma B cells of the immune system have prominent Golgi complexes.
In all eukaryotes, each cisternal stack has a cis entry face and a trans exit face. These faces are characterized by unique morphology and biochemistry.[10] Within individual stacks are assortments of enzymes responsible for selectively modifying protein cargo. These modifications influence the fate of the protein. The compartmentalization of the Golgi apparatus is advantageous for separating enzymes, thereby maintaining consecutive and selective processing steps: enzymes catalyzing early modifications are gathered in the cis face cisternae, and enzymes catalyzing later modifications are found in trans face cisternae of the Golgi stacks.[5][10]
Function

The Golgi apparatus is a major collection and dispatch station of protein products received from the endoplasmic reticulum. Proteins synthesized in the ER are packaged into vesicles, which then fuse with the Golgi apparatus. These cargo proteins are modified and destined for secretion via exocytosis or for use in the cell. In this respect, the Golgi can be thought of as similar to a post office: it packages and labels items which it then sends to different parts of the cell or to the extracellular space. The Golgi apparatus is also involved in lipid transport and lysosome formation.[11]
The structure and function of the Golgi apparatus are intimately linked. Individual stacks have different assortments of enzymes, allowing for progressive processing of cargo proteins as they travel from the cisternae to the trans Golgi face.[5][10] Enzymatic reactions within the Golgi stacks occur exclusively near its membrane surfaces, where enzymes are anchored. This feature is in contrast to the ER, which has soluble proteins and enzymes in its lumen. Much of the enzymatic processing is post-translational modification of proteins. For example, phosphorylation of oligosaccharides on lysosomal proteins occurs in the early CGN.[5] Cis cisterna are associated with the removal of mannose residues.[5][10] Removal of mannose residues and addition of N-acetylglucosamine occur in medial cisternae.[5] Addition of galactose and sialic acid occurs in the trans cisternae.[5] Sulfation of tyrosines and carbohydrates occurs within the TGN.[5] Other general post-translational modifications of proteins include the addition of carbohydrates (glycosylation)[12] and phosphates (phosphorylation). Protein modifications may form a signal sequence that determines the final destination of the protein. For example, the Golgi apparatus adds a mannose-6-phosphate label to proteins destined for lysosomes. Another important function of the Golgi apparatus is in the formation of proteoglycans. Enzymes in the Golgi append proteins to glycosaminoglycans, thus creating proteoglycans.[13] Glycosaminoglycans are long unbranched polysaccharide molecules present in the extracellular matrix of animals.
Vesicular transport

The vesicles that leave the rough endoplasmic reticulum are transported to the cis face of the Golgi apparatus, where they fuse with the Golgi membrane and empty their contents into the lumen. Once inside the lumen, the molecules are modified, then sorted for transport to their next destinations.
Those proteins destined for areas of the cell other than either the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi apparatus are moved through the Golgi cisternae towards the trans face, to a complex network of membranes and associated vesicles known as the trans-Golgi network (TGN). This area of the Golgi is the point at which proteins are sorted and shipped to their intended destinations by their placement into one of at least three different types of vesicles, depending upon the signal sequence they carry.
| Types | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Exocytotic vesicles (constitutive) | Vesicle contains proteins destined for extracellular release. After packaging, the vesicles bud off and immediately move towards the plasma membrane, where they fuse and release the contents into the extracellular space in a process known as constitutive secretion. | Antibody release by activated plasma B cells |
| Secretory vesicles (regulated) | Vesicles contain proteins destined for extracellular release. After packaging, the vesicles bud off and are stored in the cell until a signal is given for their release. When the appropriate signal is received they move toward the membrane and fuse to release their contents. This process is known as regulated secretion. | Neurotransmitter release from neurons |
| Lysosomal vesicles | Vesicles contain proteins and ribosomes destined for the lysosome, a degradative organelle containing many acid hydrolases, or to lysosome-like storage organelles. These proteins include both digestive enzymes and membrane proteins. The vesicle first fuses with the late endosome, and the contents are then transferred to the lysosome via unknown mechanisms. | Digestive proteases destined for the lysosome |
Current models of vesicular transport and trafficking
Model 1: Anterograde vesicular transport between stable compartments
- In this model, the Golgi is viewed as a set of stable compartments that work together. Each compartment has a unique collection of enzymes that work to modify protein cargo. Proteins are delivered from the ER to the cis face using COPII-coated vesicles. Cargo then progress toward the trans face in COPI-coated vesicles. This model proposes that COPI vesicles move in two directions: anterograde vesicles carry secretory proteins, while retrograde vesicles recycle Golgi-specific trafficking proteins.[14]
- Strengths: The model explains observations of compartments, polarized distribution of enzymes, and waves of moving vesicles. It also attempts to explain how Golgi-specific enzymes are recycled.[14]
- Weaknesses: Since the amount of COPI vesicles varies drastically among types of cells, this model cannot easily explain high trafficking activity within the Golgi for both small and large cargoes. Additionally, there is no convincing evidence that COPI vesicles move in both the anterograde and retrograde directions.[14]
- This model was widely accepted from the early 1980s until the late 1990s.[14]
Model 2: Cisternal progression/maturation
- In this model, the fusion of COPII vesicles from the ER begins the formation of the first cis-cisterna of the Golgi stack, which progresses later to become mature TGN cisternae. Once matured, the TGN cisternae dissolve to become secretory vesicles. While this progression occurs, COPI vesicles continually recycle Golgi-specific proteins by delivery from older to younger cisternae. Different recycling patterns may account for the differing biochemistry throughout the Golgi stack. Thus, the compartments within the Golgi are seen as discrete kinetic stages of the maturing Golgi apparatus.[14]
- Strengths: The model addresses the existence of Golgi compartments, as well as differing biochemistry within the cisternae, transport of large proteins, transient formation and disintegration of the cisternae, and retrograde mobility of native Golgi proteins, and it can account for the variability seen in the structures of the Golgi.[14]
- Weaknesses: This model cannot easily explain the observation of fused Golgi networks, tubular connections among cisternae, and differing kinetics of secretory cargo exit.[14]
Model 3: Cisternal progression/maturation with heterotypic tubular transport
- This model is an extension of the cisternal progression/maturation model. It incorporates the existence of tubular connections among the cisternae that form the Golgi ribbon, in which cisternae within a stack are linked. This model posits that the tubules are important for bidirectional traffic in the ER-Golgi system: they allow for fast anterograde traffic of small cargo and/or the retrograde traffic of native Golgi proteins.[14][15]
- Strengths: This model encompasses the strengths of the cisternal progression/maturation model that also explains rapid trafficking of cargo, and how native Golgi proteins can recycle independently of COPI vesicles.[14]
- Weaknesses: This model cannot explain the transport kinetics of large protein cargo, such as collagen. Additionally, tubular connections are not prevalent in plant cells. The roles that these connections have can be attributed to a cell-specific specialization rather than a universal trait. If the membranes are continuous, that suggests the existence of mechanisms that preserve the unique biochemical gradients observed throughout the Golgi apparatus.[14]
Model 4: Rapid partitioning in a mixed Golgi
- This rapid partitioning model is the most drastic alteration of the traditional vesicular trafficking point of view. Proponents of this model hypothesize that the Golgi works as a single unit, containing domains that function separately in the processing and export of protein cargo. Cargo from the ER move between these two domains, and randomly exit from any level of the Golgi to their final location. This model is supported by the observation that cargo exits the Golgi in a pattern best described by exponential kinetics. The existence of domains is supported by fluorescence microscopy data.[14]
- Strengths: Notably, this model explains the exponential kinetics of cargo exit of both large and small proteins, whereas other models cannot.[14]
- Weaknesses: This model cannot explain the transport kinetics of large protein cargo, such as collagen. This model falls short on explaining the observation of discrete compartments and polarized biochemistry of the Golgi cisternae. It also does not explain formation and disintegration of the Golgi network, nor the role of COPI vesicles.[14]
Model 5: Stable compartments as cisternal model progenitors
- This is the most recent model. In this model, the Golgi is seen as a collection of stable compartments defined by Rab (G-protein) GTPases.[14]
- Strengths: This model is consistent with numerous observations and encompasses some of the strengths of the cisternal progression/maturation model. Additionally, what is known of the Rab GTPase roles in mammalian endosomes can help predict putative roles within the Golgi. This model is unique in that it can explain the observation of "megavesicle" transport intermediates.[14]
- Weaknesses: This model does not explain morphological variations in the Golgi apparatus, nor define a role for COPI vesicles. This model does not apply well for plants, algae, and fungi in which individual Golgi stacks are observed (transfer of domains between stacks is not likely). Additionally, megavesicles are not established to be intra-Golgi transporters.[14]
Though there are multiple models that attempt to explain vesicular traffic throughout the Golgi, no individual model can independently explain all observations of the Golgi apparatus. Currently, the cisternal progression/maturation model is the most accepted among scientists, accommodating many observations across eukaryotes. The other models are still important in framing questions and guiding future experimentation. Among the fundamental unanswered questions are the directionality of COPI vesicles and role of Rab GTPases in modulating protein cargo traffic.[14]
Brefeldin A
Brefeldin A (BFA) is a fungal metabolite used experimentally to disrupt the secretion pathway as a method of testing Golgi function.[16] BFA blocks the activation of some ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs).[17] ARFs are small GTPases which regulate vesicular trafficking through the binding of COPs to endosomes and the Golgi.[17] BFA inhibits the function of several guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) that mediate GTP-binding of ARFs.[17] Treatment of cells with BFA thus disrupts the secretion pathway, promoting disassembly of the Golgi apparatus and distributing Golgi proteins to the endosomes and ER.[16][17]
Gallery
-
Yeast Golgi dynamics. Green labels early Golgi, red labels late Golgi.[18]
-
Two Golgi stacks connected as a ribbon in a mouse cell. Taken from the movie.
-
Three-dimensional projection of a mammalian Golgi stack imaged by confocal microscopy and volume surface rendered using Imaris software. Taken from the movie.
References
- ^ Pavelk M, Mironov AA (2008). "Golgi apparatus inheritance". The Golgi Apparatus: State of the art 110 years after Camillo Golgi's discovery. Berlin: Springer. p. 580. doi:10.1007/978-3-211-76310-0_34. ISBN 978-3-211-76310-0.
- ^ a b c d e Fabene PF, Bentivoglio M (October 1998). "1898-1998: Camillo Golgi and "the Golgi": one hundred years of terminological clones". Brain Research Bulletin. 47 (3): 195–8. doi:10.1016/S0361-9230(98)00079-3. PMID 9865849. S2CID 208785591.
- ^ Golgi C (1898). "Intorno alla struttura delle cellule nervose" (PDF). Bollettino della Società Medico-Chirurgica di Pavia. 13 (1): 316. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-04-07.
- ^ a b Davidson MW (2004-12-13). "The Golgi Apparatus". Molecular Expressions. Florida State University. Archived from the original on 2006-11-07. Retrieved 2010-09-20.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Alberts, Bruce; et al. (1994). Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8153-1619-0.
- ^ a b c d e Nakano A, Luini A (August 2010). "Passage through the Golgi". Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 22 (4): 471–8. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2010.05.003. PMID 20605430.
- ^ Suda Y, Nakano A (April 2012). "The yeast Golgi apparatus". Traffic. 13 (4): 505–10. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01316.x. PMID 22132734.
- ^ Duran JM, Kinseth M, Bossard C, Rose DW, Polishchuk R, Wu CC, Yates J, Zimmerman T, Malhotra V (June 2008). "The role of GRASP55 in Golgi fragmentation and entry of cells into mitosis". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 19 (6): 2579–87. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-10-0998. PMC 2397314. PMID 18385516.
- ^ Day, Kasey J.; Casler, Jason C.; Glick, Benjamin S. (2018). "Budding Yeast Has a Minimal Endomembrane System". Developmental Cell. 44 (1): 56–72.e4. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2017.12.014. PMC 5765772. PMID 29316441.
- ^ a b c d Day KJ, Staehelin LA, Glick BS (September 2013). "A three-stage model of Golgi structure and function". Histochemistry and Cell Biology. 140 (3): 239–49. doi:10.1007/s00418-013-1128-3. PMC 3779436. PMID 23881164.
- ^ Campbell, Neil A (1996). Biology (4 ed.). Menlo Park, CA: Benjamin/Cummings. pp. 122, 123. ISBN 978-0-8053-1957-6.
- ^ William G. Flynne (2008). Biotechnology and Bioengineering. Nova Publishers. pp. 45–. ISBN 978-1-60456-067-1. Retrieved 13 November 2010.
- ^ Prydz K, Dalen KT (January 2000). "Synthesis and sorting of proteoglycans". Journal of Cell Science. 113. 113 Pt 2 (2): 193–205. doi:10.1242/jcs.113.2.193. PMID 10633071.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Glick BS, Luini A (November 2011). "Models for Golgi traffic: a critical assessment". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 3 (11): a005215. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a005215. PMC 3220355. PMID 21875986.
- ^ Wei JH, Seemann J (November 2010). "Unraveling the Golgi ribbon". Traffic. 11 (11): 1391–400. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01114.x. PMC 4221251. PMID 21040294.
- ^ a b Marie M, Sannerud R, Avsnes Dale H, Saraste J (September 2008). "Take the 'A' train: on fast tracks to the cell surface". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 65 (18): 2859–74. doi:10.1007/s00018-008-8355-0. PMC 7079782. PMID 18726174.
- ^ a b c d D'Souza-Schorey C, Chavrier P (May 2006). "ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 7 (5): 347–58. doi:10.1038/nrm1910. PMID 16633337. S2CID 19092867.
- ^ Papanikou E, Day KJ, Austin J, Glick BS (2015). "COPI selectively drives maturation of the early Golgi". eLife. 4. doi:10.7554/eLife.13232. PMC 4758959. PMID 26709839.
External links
 Media related to Golgi apparatus at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Golgi apparatus at Wikimedia Commons


