1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran
This article needs attention from an expert in Chemistry. The specific problem is: Lots of missing key reagents in images and incorrect/confusing (possibly "non-chemist translation engine"?) chemical terminology. (September 2019) |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Diphenyl-2-benzofuran | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.371 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C20H14O | |
| Molar mass | 270.33 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | pale yellow[1] to dark yellow crystalline powder[2] |
| Density | 1.0717 g·cm−3 bei 25 °C[3] |
| Melting point | * 125–126 °C[4]
|
| almost insoluble | |
| Solubility in acetonitrile, benzene, dichloromethane, chloroform, dimethylsulfoxide, tetrahydrofuran or toluene | soluble[5] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran is a highly reactive diene that can scavenge unstable and short-lived dienophiles in a Diels-Alder reaction. It is furthermore used as a standard reagent[6] for the determination of singlet oxygen,[7] even in biological systems.[8] Cycloadditions with 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran and subsequent oxygen cleavage provide access to a variety of polyaromatics.
Preparation
[edit]The first synthesis of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran was reported in 1905 by A. Guyot and J. Catel.[9][10] Phenylmagnesium bromide was reacted with 3-phenylphthalide (the latter accessible from the methyl ester of 3-hydroxyphthalide with phenylboronic acid in 95% yield[11]) to a lactol, which gives with mineral acids upon elimination of water 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran with 87% yield.[12]

The patent literature describes the preparation of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran by [4+2]cycloaddition of 1,3-butadiene and dibenzoylethylene (1,4-diphenyl-2-butene-1,4-dione, accessible from fumaryl chloride and benzene in the presence of aluminium chloride.[13]).[14] Dibenzoylethylene is predominantly present in the trans configuration[15] but it can be converted into the needed cis configuration by simple heating.[16]

The 4,5-dibenzoylcyclohexene formed previously is cyclized with acetic anhydride to the dihydroisobenzofuran. By bromine addition and hydrogen bromide elimination, 1,2-dibenzoylbenzene is formed and recyclized with zinc acetic acid to the final product 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran.[17] A publication from 1940 describes high yields for the individual stages of the extensive reaction sequence.[4]
The (much cheaper) phthaloyl chloride gives also access to 1,2-dibenzoylbenzene via Friedel-Crafts acylation with benzene,[18] which is reduced to 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran in 78% yield using potassium borohydride.[19]

The synthesis of 1,3-diarylisobenzofurans from 2-acylbenzaldehydes and boronic acids is less cumbersome and gives better yields,[20]

just like the synthesis from salicylaldehydes via phenacylhydrazones, which undergo oxidation with lead(IV) acetate to give ortho-diketones,[21] followed by the reaction with an aryl Grignard reagent.[22]

Properties
[edit]1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran is a yellow, light- and air-sensitive, crystalline solid that is soluble in many organic solvents with a maximum absorption around 420 nm (in solution), which generates intense fluorescence.[23] Fluorescence measurements can be performed in DMF and DMSO because of the stability of 1,3-DPBF in those solvents. In chloroform and carbon tetrachloride the dissolved 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran is rapidly photolyzed by attack of CHCl2 and CCl3 radicals, even in the absence of oxygen.[24] [24 ]
With ethanol, 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran forms an orange-yellow, fluorescent solution. On irradiation, it forms a colorless photodimer (upon with exclusion of oxygen), upon discolouration of the solution.[25]

The compound's refractive index is 1,6700 at 25 °C and 589 nm.[3]
Use
[edit]Reagent for determination of singlet oxygen
[edit]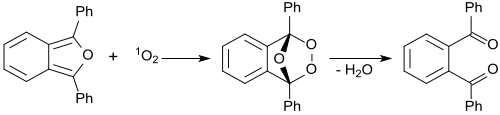


In the presence of methylene blue irradiated with red laser light, 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran reacts with intermediate singlet oxygen 1O2, forming an unstable peroxide that decomposes into (colorless) 1,2-dibenzoylbenzene.[27] The detection of singlet oxygen by 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran is based on this reaction, even in biological systems. For biological systems, water-soluble derivatives of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran were developed.[28] The singlet oxygen generation of photosensitizers were monitored by photolysis of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran (DPBF). 1,2-Dibenzoylbenzene absorbs at <300 nm, therefore making DPBF an optimal chemical trap for detecting singlet oxygen, as most photosensitizers absorb <400-600 nm. This allows for an accurate determination of the photodegradation of the molecule.
Dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions
[edit]Isobenzofurans like 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran are among the most reactive Diels-Alder dienes known to date,[29] and are useful for scavenging short-lived and unstable olefins and alkynes. The group led by Georg Wittig made important contributions to this topic.
With the unstable cyclohexyne, 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran reacts to a tricyclic compound that gives a 9,10-diphenylcyclohexenonaphthalene after hydrogenation and hydrogen abstraction.[30]

1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran gives similarly with benzyne (dehydrobenzene) an oxygen-bridged anthracene (in 85% yield), which can be reduced with zinc to 9,10-diphenylanthracene (88% yield).[31]

Cyclopropenone (which is unstable above its melting point of -29 °C) reacts quantitatively at room temperature with 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran to form a Diels-Alder adduct,[32] which is exclusively an exo isomer.[33]

Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate reacts with 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran as dienophile in 84% yield to yield the corresponding adduct.[34]

1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran reacts also with heterocyclic dienophiles such as 3-sulfolene to the corresponding Diels-Alder adduct.[35]
Molecular building block for polyaromatics
[edit]Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are of interest as precursors to graphite but also raise concern as ingredients of pollution. They have persistence and carcinogenicity. 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran reacts quantitatively with acenaphthylene when heated to 160 °C to give 7,12-diphenylbenzo[k]fluoranthene.[36]

The twice occurring Diels-Alder reaction of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran with p-benzoquinone yields almost quantitatively a product that can be reacted further with p-toluenesulfonic acid to give a pentacene derivative in 49% yield.[37]

Literature
[edit]- W. Friedrichsen (1980), "Benzo[c]furans", Adv. Heterocycl. Chem., Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry, vol. 26, pp. 135–234, doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60141-5, ISBN 9780120206261
- W. Friedrichsen (1999), "Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Benzo[c]furans and Related Compounds", Adv. Heterocycl. Chem., Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry, vol. 73, pp. 1–96, doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60940-X, ISBN 9780120207732
- R. Rodrigo (1988), "Progress in the chemistry of isobenzofurans: Applications to the synthesis of natural products and polyaromatic hydrocarbons", Tetrahedron, vol. 44, no. 8, pp. 2093–2135, doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)81720-8
References
[edit]- ^ "1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran 5471-63-6 | TCI Deutschland GmbH". www.tcichemicals.com (in German). Retrieved 2018-01-14.
- ^ a b Sigma-Aldrich Co., product no. 105481.
- ^ a b Carl L. Yaws (2015), Thermophysical Properties of Chemicals and Hydrocarbons, 2nd Edition, Oxford, UK: Elsevier Inc., p. 604, ISBN 978-0-323-28659-6
- ^ a b R. Adams; M.H. Gold (1940), "The Synthesis of 1,3-Diphenyldihydroisobenzofurans, 1,3-Diphenylisobenzofurans and o-Dibenzoylbenzenes from the Diene Addition Products to Dibenzoylethylene", Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 56–61, doi:10.1021/ja01858a012
- ^ P.C. Kierkus (2001), "1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran", E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd420, ISBN 0471936235
- ^ R.H. Young; K. Wehrly; R.L. Martin (1971), "Solvent effects in dye-sensitized photooxidation reactions", Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 93, no. 22, pp. 5774–5779, doi:10.1021/ja00751a031
- ^ J.A. Howard; G.D. Mendenhall (1975), "Autoxidation and photooxidation of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran: A kinetic and product study", Canadian Journal of Chemistry, vol. 53, no. 14, pp. 2199–2201, doi:10.1139/v75-307
- ^ P. Carloni; et al. (1993), "On the use of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran (DPBF). Reactions with carbon and oxygen centered radicals in model and natural systems", Res. Chem. Intermed., vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 395–405, doi:10.1163/156856793X00181, S2CID 94802096
- ^ A. Guyot, J. Catel, Bull. Soc. Chim. France, [3] (35), 1124 (1906)
- ^ A. Guyot, J. Catel, Compt. Rend. Hebd. Acad. Sci., Ser. C140, 1348 (1905)
- ^ M. Kuriyama; N. Ishiyama; R. Shimazawa; R. Shirai; O. Onomura (2009), "Efficient synthesis of 3-arylphthalides using palladium-catalyzed arylation of aldehydes with organoboronic acids", Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 74, no. 23, pp. 9210–9213, doi:10.1021/jo901964k, PMID 19873994
- ^ M. S. Newman (1961), "Evidence favoring a two-step mechanism for the Diels-Alder reaction", Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 26, no. 8, pp. 2630–2633, doi:10.1021/jo01066a004
- ^ "trans-Dibenzoylethylene". Organic Syntheses. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.020.0029.
- ^ US 2325727, R. Adams, "Dehydroisobenzofurans and process for preparing them", published 1943-08-03, assigned to E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co.
- ^ "1,2-Dibenzoylethylene, predominantly trans, 96%". Thermo Scientific Chemicals.
- ^ D.V. Klemm; A. Tuncay (1989), "Photochemical and thermal isomerization of trans- and cis-1,2-dibenzoylethylene: A microscale approach", J. Chem. Educ., vol. 66, no. 6, p. 519, Bibcode:1989JChEd..66..519K, doi:10.1021/ed066p519
- ^ US 2356907, R. Adams, "1,3-Diphenylisobenzofurans and process for preparing the same", published 1944-08-29, assigned to E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co.
- ^ Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry (1973), Organometallic Compounds of Group II of the Periodic Table, 4th Edition, vol. XIII/2a, Stuttgart: Thieme, p. 419, ISBN 978-3-13-213204-7
- ^ M. Cava; M.J. Mitchell; A.A. Deana (1960), "Condensed cyclobutane aromatic compounds. XIII. An attempted synthesis of 1,2-diphenylbenzocyclobutene", Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 25, no. 9, pp. 1481–1484, doi:10.1021/jo01079a005
- ^ J. Jacq; B. Bessières; C. Einhorn; J. Einhorn (2010), "Regiospecific synthesis of functionalised 1,3-diarylisobenzofurans via palladium- and rhodium-catalysed reaction of boronic acids with o-acylbenzaldehydes under thermal or microwave activation", Org. Biomol. Chem., vol. 8, no. 21, pp. 4927–4933, doi:10.1039/c0ob00110d, PMID 20740250
- ^ A. Kotali; P.G. Tsoungas (1987), "Oxidation of N-aroylhydrazones of o-hydroxyaryl ketones with lead(IV)acetate: A facile route to aromatic o-diketones", Tetrahedron Lett., vol. 28, no. 37, pp. 4321–4322, doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)96497-9
- ^ J. Jacq; C. Einhorn; J. Einhorn (2008), "A versatile and regiospecific synthesis of functionalised 1,3-diarylisobenzofurans", Org. Lett., vol. 10, no. 17, pp. 3757–3760, doi:10.1021/ol801550a, PMID 18666776
- ^ M. Wozniak; F. Tanfani; E. Bertoli; G. Zolese; J. Antonsiewicz (1991), "A new fluorescence method to detect singlet oxygen inside phospholipid model membranes", Biochim. Biophys. Acta, vol. 1082, no. 1, pp. 94–100, doi:10.1016/0005-2760(91)90304-Z, PMID 1849016
- ^ X.-F. Zhang; X. Liu (2011), "The photostability and fluorescence properties of diphenylisobenzofuran", Journal of Luminiscence, vol. 131, no. 11, pp. 2263–2266, Bibcode:2011JLum..131.2263Z, doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2011.05.048
- ^ A. Schönberg; A. Mustafa; G. Aziz (September 1, 1954), "Diels-Alder Reaction. II. Experiments with 2-Styrylchromones. On the Nature of the Dimer of 1,3-Diphenylisobenzofuran", Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 76, no. 18, pp. 4576–4577, doi:10.1021/ja01647a020
- ^ Soman, Rahul; Raghav, Darpan; Sujatha, Subramaniam; Rathinasamy, Krishnan; Arunkumar, Chellaiah (30 Jun 2015). "Axial ligand modified high valent tin(iv) porphyrins: synthesis, structure, photophysical studies and photodynamic antimicrobial activities on Candida albicans". RSC Adv. 5 (75): 61103. Bibcode:2015RSCAd...561103S. doi:10.1039/C5RA09343K.
- ^ "Grundpraktikum Physikalische Chemie, V28, Photooxidation von Diphenylisobenzofuran, Untersuchung der Reaktionskinetik durch Photometrie" (PDF) (in German). Universität Ulm. 2010-12-06. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-05-17. Retrieved 2017-08-30.
- ^ C. Schmitz; J.M. Aubry; J. Rigaudy (1982), "A new access to the anthracene core: Synthesis of two water soluble singlet oxygen traps derived from 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran and 9,10-diphenylanthracene", Tetrahedron, vol. 38, no. 10, pp. 1425–1430, doi:10.1016/0040-4020(82)80224-X
- ^ D. Tobia; B. Rickborn (1987), "Substituent effects on rates of inter- and intramolecular cycloaddition reactions of isobenzofurans", Journal of Organic Chemistry, vol. 52, no. 12, pp. 2611–2615, doi:10.1021/jo00388a055
- ^ G. Wittig (1963), "Über kleine Ringe mit Kohlenstoffdreifachbindung – noch eine Chemie des "Als ob"", Pure Appl. Chem. (in German), vol. 7, no. 2–3, pp. 173–192, doi:10.1351/pac196307020173, S2CID 95499778
- ^ G. Wittig; E. Knauss; K. Niethamer (1960), "Über 9,10-Dihydroanthracen-Derivate mit Heterobrückenatomen", Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. (in German), vol. 630, no. 1, pp. 10–18, doi:10.1002/jlac.19606300103
- ^ R. Breslow; M. Oda (1972), "Isolation and characterization of pure cyclopropenone", Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 94, no. 13, pp. 4787–4788, doi:10.1021/ja00768a089
- ^ "Exo selectivity of the Diels-Alder addition of cyclopropenone and 1-3-diphenylisobenzofuran". Retrieved 2017-08-28.
- ^ J.A. Berson (1953), "Reactions of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran with acetylenic dienophiles", Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 75, no. 5, pp. 1240–1241, doi:10.1021/ja01101a503
- ^ M.P. Cava; J.P. VanMeter (1969), "Condensed cyclobutane aromatic compounds. XXX. Synthesis of some unusual 2,3-naphthoquinonoid heterocycles. A synthetic route to derivatives of naphtho[2,3-b]biphenylene and anthra[b]cyclobutene", Journal of Organic Chemistry. Org. Chem., vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 538–545, doi:10.1021/jo01255a012
- ^ Houben-Weyl Science of Synthesis (2009), Compounds with All-Carbon Functions, vol. 45b, Stuttgart: Thieme, p. 1038, ISBN 978-3-13-146551-1
- ^ G.P. Miller; J. Briggs (2002), "Progress towards the synthesis of tris- and tetrakis[60]fullerene adducts", Electrochem. Soc. Proc., vol. 2002–12, pp. 279–284, ISBN 1-56677-333-4
