Hesperocyparis stephensonii
| Hesperocyparis stephensonii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Cupressales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Hesperocyparis |
| Species: | H. stephensonii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hesperocyparis stephensonii (C.B.Wolf) Bartel
| |
| |
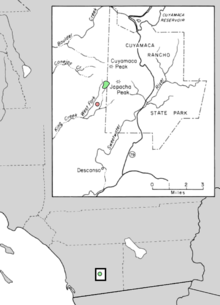
| Natural range of Hesperocyparis stephensonii | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Hesperocyparis stephensonii is a species of western cypress known as the Cuyamaca cypress that is found only in one very small area in Southern California.
Distribution
[edit]The Cuyamaca Cypress only verifiably exists in the headwaters area of King Creek in the Cuyamaca Mountains of the Peninsular Ranges system, south of Cuyamaca Peak within San Diego County in extreme Southern California.[3][4]
Trees were reported growing as low as 3,000 feet (910 m) in elevation in 1998, but the presence of these individuals today has not been verified.[5] Most individual trees occur at 4,500–5,100 feet (1,400–1,600 m) within the Pacific Southwest Research Station's King Creek Research Natural Area, in the Cleveland National Forest.[6][7][8]
Conservation
[edit]It is an IUCN Red List Critically Endangered species, and a California Native Plant Society Inventory of Rare and Endangered Plants listed Seriously endangered species.[1][9] The entire native (world) population of the tree was reduced down to thirty to forty individual trees by the 2003 Cedar Fire.[10]
Description
[edit]
note the very subtle differences in bark color and texture from H. glabra and H. forbesii.
Hesperocyparis stephensonii may attain heights of 10 to 16 m (33 to 52 ft).[6] It usually forms a spreading tree with a central leader, only slightly taller than it is wide.
The tree's female cones are about 10 mm in diameter, while cone scales are normally 6–8 mm. Often, but not always, they have conspicuous umbos 3–4 mm, which are high and conical. There are normally 100-125 seeds per cone, not at all glaucous. 3-4 cotyledons are usually present. It is the only western cypress species in California to release pollen in the summertime.[7][4]
Taxonomy
[edit]Hesperocyparis stephensonii was not given a scientific description until 1948. In that year Carl Brandt Wolf published a paper and gave it the name Cupressus stephensonii.[2][11] At that time it was standard for species classified in Hesperocyparis to be classified as part of a larger Cupressus genus that covered both new and old world species. Though somewhat distinct there was disagreement on its correct classification with it being described as a variety of Cupressus arizonica in 1966 and in 1982 as a subspecies of the same.[2]
In the 2000s new genetic research called into question the classification of New World cypress trees. In 2009 a paper was published by Jim A. Bartel that reclassified most of the North American species into the new genus Hesperocyparis. By the year 2017 this classification was being used by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS database,[12] California Native Plant Society,[13] and University and Jepson Herbaria.[14]
In the past there has been considerable debate about the status of Hesperocyparis stephensonii as a species and some sources continue to use classifications such as Cupressus arizonica var. stephensonii.[6][15] As of 2024[update] Hesperocyparis stephensonii is recognized as an accepted species by Plants of the World Online,[2] World Flora Online,[16] and the Gymnosperm Database.[6]
Names
[edit]Wolf named the species stephensonii to honor Bert Stephenson, a ranger with the US Forest Service who died in 1944. Ranger Stephenson had noticed the trees on King Creek while fighting a forest fire in the area and informed Wolf about them.[11] The common name "Cuyamaca cypress" comes from its native habitat on Cuyamaca Peak.[4]
See also
[edit]- Hesperocyparis forbesii — nearby endemic Cypress/Hesperocyparis sp.
- Flora of the California chaparral and woodlands
- Natural history of the Peninsular Ranges
References
[edit]- ^ a b Farjon, A. (16 March 2011). "Cupressus arizonica var. stephensonii:". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013: e.T33999A2839907. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T33999A2839907.en. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ a b c d "Hesperocyparis stephensonii (C.B.Wolf) Bartel". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ^ "Hesperocyparis stephensonii". The Calflora Database. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ a b c Lanner, Ronald M. (1999). Conifers of California. Los Olives, California: Cachuma Press. pp. 192–193. ISBN 978-0-9628505-3-0. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ Wolf
- ^ a b c d Earle, Christopher J. (17 December 2023). "Hesperocyparis stephensonii (Cuyamaca cypress) description". The Gymnosperm Database. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ a b Bartel, Jim A. "Hesperocyparis stephensonii". Jepson eFlora. The Jepson Herbarium University of California, Berkeley. Archived from the original on 24 February 2024. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ USFS: King Creek Research Natural Area
- ^ California Native Plant Society, Inventory of Rare and Endangered Plants (online edition, v8-02): Hesperocyparis stephensonii . accessed 2 February 2017.
- ^ Downey, Dave (16 November 2003). "Firestorm 2003: The story of a catastrophe". San Diego Union-Tribune. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
Downey, Dave (23 November 2003). "Some rare trees survived fire". San Diego Union-Tribune. Retrieved 16 February 2018. - ^ a b Wolf, Carl B. (1948). "Taxonomic and Distributional Studies of the New World Cypresses". Aliso: A Journal of Systematic and Floristic Botany. 1 (1): 125–127. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ Hesperocyparis stephensonii, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Profile, 27 February 2024
- ^ "Calflora: Hesperocyparis stephensonii". Wayback Machine. Archive.org. 8 February 2017. Archived from the original on 8 February 2017. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Jepson Herbarium: Jepson Flora Project: Jepson eFlora: Hesperocyparis stephensonii". Wayback Machine. Archive.org. 8 February 2017. Archived from the original on 8 February 2017. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Farjon, A. (2019). "Cupressus arizonica var. stephensonii". Threatened Conifers of the World, The International Conifer Conservation Programme. Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ "Hesperocyparis stephensonii (C.B.Wolf) Bartel". World Flora Online. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
Further reading
[edit]- Wolf, C. B. & Wagener, W. E. (1948). The New World Cypresses. El Aliso 1: 195-205.
- palomar.edu: The True Cypresses (Genus Cupressus = Callitropsis) "Isolated Groves In Western North America" - (web.article)
External links
[edit]- CalFlora Database: Hesperocyparis stephensonii (Cuyamaca cypress) — formerly Cupressus stephensoniia.
- Jepson eFlora (TJM2) treatment of Hesperocyparis stephensonii — ''formerly Cupressus stephensoniia + Cupressus arizonica var. glabra.
- USDA Plants Profile for Hesperocyparis stephensonii (Cuyamaca cypress) — formerly Cupressus stephensonii + Cupressus arizonica subsp. stephensonii.
- Conifers.org - Cupressus stephensonii
- Cupressus.net: Images of Cupressus stephensonii
- Pacific Southwest Research Stations, Cleveland National Forest King Creek Research Natural Area — with in-situ photos + info.
- UC CalPhotos gallery of Hesperocyparis stephensonii
- IUCN Red List critically endangered species
- Hesperocyparis
- Trees of Northern America
- Cuyamaca Mountains
- Natural history of the California chaparral and woodlands
- Natural history of the Peninsular Ranges
- Natural history of San Diego County, California
- Cleveland National Forest
- Plants described in 1948
- Critically endangered flora of California

