Midlothian
| |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 55°53′39″N 3°04′07″W / 55.89417°N 3.06861°W | |
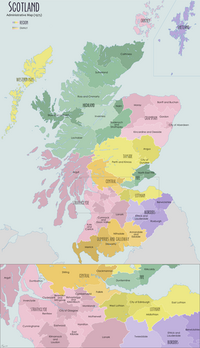
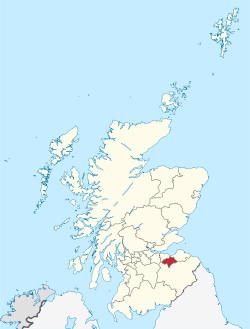
| Country | Scotland |
| Lieutenancy area | Midlothian |
| Admin HQ | Dalkeith |
| Government | |
| • Body | Midlothian Council |
| • Control | SNP minority (council NOC) |
| • MPs |
|
| • MSPs |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 137 sq mi (354 km2) |
| • Rank | Ranked 21st |
| Population (2022) | |
| • Total | 97,030 |
| • Rank | Ranked 23rd |
| • Density | 710/sq mi (270/km2) |
| ONS code | S12000019 |
| ISO 3166 code | GB-MLN |
| Largest town | Penicuik |
| Website | www |
Midlothian (/mɪdˈloʊðiən/; Scottish Gaelic: Meadhan Lodainn) is a historic county, registration county, lieutenancy area and one of 32 council areas of Scotland used for local government. Midlothian lies in the east-central Lowlands, bordering the City of Edinburgh council area, East Lothian and the Scottish Borders.
Midlothian emerged as a county in the Middle Ages under larger boundaries than the modern council area, including Edinburgh itself. The county was formally called the "shire of Edinburgh" or Edinburghshire until the twentieth century. It bordered West Lothian to the west, Lanarkshire, Peeblesshire and Selkirkshire to the south, and East Lothian, Berwickshire and Roxburghshire to the east. Traditional industries included mining, agriculture and fishing—although the modern council area is now landlocked.
History
[edit]It has been suggested that this section be split out into another article titled Midlothian (historic). (Discuss) (January 2024) |

Following the end of the Roman occupation of Britain, Lothian was populated by Brythonic-speaking ancient Britons and formed part of Gododdin, within the Hen Ogledd or Old North. In the seventh century, Gododdin fell to the Angles, with Lothian becoming part of the kingdom of Bernicia. Bernicia united into the Kingdom of Northumbria which itself became part of the early Kingdom of England. Lothian came under the control of the Scottish monarchy in the tenth century.
In the Middle Ages, Lothian was the scene of several historic conflicts between the kingdoms of Scotland and England. The Battle of Roslin took place in 1303 at Roslin as part of the First War of Scottish Independence. A Scottish army led by Simon Fraser and John Comyn defeated an army led by English commander John Segrave.
Along with other parts of the Lothians, the county was involved in the Rough Wooing when Roslin Castle, seat of the Earl of Caithness, was destroyed in 1544 by forces of Henry VIII of England.
In the 17th century, the county featured in the War of the Three Kingdoms, where General George Monck had his base at Dalkeith Castle as the Commonwealth's Commander in Scotland.[1] Following the Restoration of the monarchy, the "Pentland Rising" in the region culminated with the Battle of Rullion Green in 1666, a decisive victory for the Government forces against Covenanter rebels.
In 1650, Oliver Cromwell's army came to Dalkeith. His officer General George Monck, was Commander in Scotland, and the government of the country was based out of Dalkeith castle.[2]
The 1878-80 Midlothian campaign by British Liberal politician William Ewart Gladstone entered history as an early example of modern political campaigning, resulting in Gladstone taking the Midlothian constituency from the long-time Conservative Member of Parliament William Montagu Douglas Scott and going on to become Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
On 1 June 1978, Midlothian became Sister Cities with Midlothian, Illinois.
Governance
[edit]The modern council area of Midlothian is governed by Midlothian Council, based in Dalkeith.

Shire and county
[edit]The origins of the historic county of Midlothian are obscure; it emerged as a shire (the area controlled by a sheriff) in the Middle Ages, and was certainly in existence by the reign of David I (reigned 1124–1153). It covered the central part of the former kingdom or province of Lothian, and was formally called the "shire of Edinburgh" or "Edinburghshire", although the alternative name "Midlothian" was also used from a very early date. The burgh of Edinburgh became administratively independent from the surrounding county in 1482 when James III granted the burgh the right to appoint its own sheriff and coroner, making it a county of itself.[3]
Commissioners of Supply were established for each shire in 1667, and served as the main administrative body for the county until elected county councils were created in 1890 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889, taking most of the commissioners' functions.[4] The commissioners for Edinburghshire, and the county council which followed them, did not have jurisdiction over the city of Edinburgh, which was administered by the town council of the burgh.[5]
From its creation in 1890 the county council called itself "Midlothian County Council".[6] However, the legal name of the county remained the "county of Edinburgh" or "Edinburghshire". In 1913 the county council petitioned the government to formally change the name to Midlothian.[7] The government responded that it would direct all government departments to use Midlothian rather than Edinburghshire, but that a formal change of name needed to be done by statute and it could not justify the parliamentary time to make such a change.[8] The statutory change of name from Edinburghshire to Midlothian eventually took place in 1947, under section 127 of the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1947 (10 & 11 Geo. 6. c. 43).[9]
Midlothian County Council was based at Midlothian County Buildings, built in 1904 on George IV Bridge in Edinburgh on the site of the earlier County Buildings.[10]
Midlothian was abolished as a county for local government purposes in 1975. The boundaries of the historic county of Midlothian, including the city of Edinburgh, are still used for some limited official purposes connected with land registration, being a registration county.[11]
District
[edit]Midlothian County Council was abolished in 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, which abolished Scotland's counties and burghs as administrative areas and created a new two-tier system of upper-tier regions and lower-tier districts. Most of Midlothian's territory went to a new district called Midlothian within the Lothian region. The Midlothian district was smaller than the area of the pre-1975 county, with the parts of the pre-1975 county going to other districts being:[12][13]
- Currie, Balerno, Ratho and Newbridge to the city of Edinburgh.
- Musselburgh burgh and parish of Inveresk (which included the villages of Inveresk, Wallyford and Whitecraig) to East Lothian.
- The Calders (East Calder, Midcalder and West Calder) and the Midlothian part of Livingston to West Lothian.
- Heriot and Stow parishes to the Ettrick and Lauderdale district of the Borders region.
For lieutenancy purposes, the last lord-lieutenant of the county of Midlothian was made lord-lieutenant for the new district of Midlothian when the reforms came into effect in 1975.[14] The former county council's headquarters in Edinburgh became the offices of the new Lothian Regional Council, whilst the Midlothian District Council established its headquarters in Dalkeith.[15] In 1991 the council built itself a new headquarters called Midlothian House at 40-46 Buccleuch Street in Dalkeith.[16]
Council area
[edit]
The Lothian region was abolished in 1996. The four districts in the region, including Midlothian, became unitary council areas.[17] The reconstituted Midlothian Council continues to be based at Midlothian House in Dalkeith. The Midlothian lieutenancy area corresponds to the current council area rather than the historic county.[18]
Central government
[edit]There is a Midlothian constituency of the House of Commons.
There was a Midlothian constituency of the Scottish Parliament up to the 2011 elections when it was divided between Midlothian North and Musselburgh and Midlothian South, Tweeddale and Lauderdale.
Geography
[edit]
The Midlothian council area contains the towns of Dalkeith, Bonnyrigg and Penicuik, as well as a portion of the Pentland Hills Regional Park, Rosslyn Chapel and Dalkeith Palace.
The historic county has a roughly trapezoidal shape; it consists of a fairly flat area along the Firth of Forth, which is heavily urbanised and dominated by the Edinburgh conurbation. Off the coast lie the small islands of Inchmickery and Cramond Island. The land gradually rises to the south, with the Pentland Hills in the south-west, Moorfoot Hills in the centre-south and the Lammermuir Hills in the far south-east. Blackhope Scar on the border with Peeblesshire is the highest point in the county at 651 m (2,136 ft). The county contains no lochs of any size, though there are many reservoirs, most notably Gladhouse Reservoir, Rosebery Reservoir, Edgelaw Reservoir, Loganlea Reservoir, Glencorse Reservoir, Threipmuir Reservoir, Harlaw Reservoir, Harperrig Reservoir, Crosswood Reservoir, Morton Reservoir and Cobbinshaw Reservoir.
Settlements
[edit]
Largest settlements by population:
| Settlement | Population (2022)[19] |
|---|---|
| Bonnyrigg |
18,320 |
| Penicuik |
16,150 |
| Dalkeith |
14,330 |
| Mayfield |
13,690 |
| Gorebridge |
8,040 |
| Loanhead |
6,820 |
| Danderhall |
3,160 |
| Rosewell |
2,020 |
| Roslin |
1,770 |
| Bilston |
1,440 |
Settlements within both historic and modern Midlothian
[edit]- Arniston
- Auchendinny
- Bilston
- Bonnyrigg
- Borthwick
- Carrington
- Cornbank
- Cousland
- Crichton
- Dalkeith
- Danderhall
- D'Arcy
- Deanburn
- Dewartown
- Easthouses
- Easter Howgate
- Edgehead
- Eight Mile Burn
- Eskbank
- Fala
- Ford
- Gorebridge
- Gowkshill
- Hillend
- Hopefield
- Howgate
- Lasswade
- Leadburn
- Loanhead
- Mayfield
- Millerhill
- Milton Bridge
- Newbattle
- Newtongrange
- Nine Mile Burn
- North Middleton
- Pathhead
- Penicuik
- Polton
- Rosewell
- Roslin
- Shawfair
- Silverburn
- Straiton
- Temple
- Whitehill
- Woodburn
Settlements historically in Midlothian but since transferred elsewhere
[edit]Transferred to the City of Edinburgh
[edit]- Abbeyhill
- Alnwickhill
- Ardmillan
- Baberton
- Balerno
- Balgreen
- Bankhead
- Barnton
- Beechmount
- Bingham
- Blackford
- Blackhall
- Bonaly
- Bonnington
- Braepark
- Broomhouse
- Broughton
- Brunstane
- Bruntsfield
- Bughtlin
- Burdiehouse
- Burghmuirhead
- The Calders
- Cameron Toll
- Cammo
- Canongate
- Canonmills
- Chesser
- Church Hill
- Clermiston
- Comely Bank
- Comiston
- Corstorphine
- Cowgate
- Craigcrook
- Craigentinny
- Craigleith
- Craiglockhart
- Craigmillar
- Craigour
- Cramond
- Crewe Toll
- Currie
- Curriehill
- Dalmahoy
- Dalry
- Davidson's Mains
- Dean Village
- Drumbrae
- Drylaw
- Duddingston
- Dumbiedykes
- East Craigs
- East Pilton
- Edinburgh
- Edinburgh Park
- Fairmilehead
- Ferniehill
- Ferry Road
- Firrhill
- Forrester
- Fountainbridge
- Gilmerton
- Gogar
- Gogarloch
- Goldenacre
- Gorgie
- Gracemount
- The Grange
- Granton
- Grassmarket
- Greenbank
- Greendykes
- Greenhill
- Haymarket
- Hermiston
- Holy Corner
- Holyrood
- Hunter's Tryst
- The Inch
- Ingliston
- Inverleith
- Jock's Lodge
- Joppa
- Juniper Green
- Kaimes
- Kingsknowe
- Lauriston
- Leith
- Liberton
- Little France
- Lochend
- Lochrin
- Longstone
- Marchmont
- Maybury
- Mayfield
- Meadowbank
- Merchiston
- Moredun
- Morningside
- Mortonhall
- Mountcastle
- Muirhouse
- Murrayfield
- Newbridge
- Newcraighall
- Newhaven
- Newington
- Niddrie
- Northfield
- Oxgangs
- Parkgrove
- Parkhead
- Piershill
- Pilrig
- Pilton
- Polwarth
- Portobello
- Powderhall
- Prestonfield
- Ratho
- Ratho Station
- Ravelston
- Redford
- Restalrig
- Riccarton
- Roseburn
- Saughton
- Sciennes
- Seafield
- Shandon
- Sighthill
- Silverknowes
- Slateford
- South Gyle
- Stenhouse
- Stockbridge
- Swanston
- Tollcross
- Torphin
- Trinity
- Turnhouse
- Warriston
- West Coates
- West Craigs
- West End
- Wester Broom
- Wester Hailes
- Western Harbour
- West Pilton
- Willowbrae
Transferred to East Lothian
[edit]
Transferred to Scottish Borders
[edit]Transferred to West Lothian
[edit]Places of interest
[edit]- Arniston House
- Borthwick Castle
- Castlelaw Fort
- Crichton Castle
- Dalhousie Castle
- Dalkeith Palace
- Flotterstone
- Hawthornden Castle
- Midlothian Snowsports Centre, Hillend
- National Mining Museum
- Loanhead Memorial Park
- Mavisbank House
- Melville Castle
- Newbattle Abbey
- Pentland Hills
- Roslin Castle
- Roslin Glen Country Park
- Roslin Institute
- Rosslyn Chapel
- Tyne-Esk Walk
- Vogrie Country Park
- Wallace's Cave
Civil parishes in the County of Midlothian
[edit](Unitary authority indicated where not Midlothian. Boundaries defined by Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973)[20][21]

- Borthwick
- Carrington
- Cockpen
- Cranston
- Crichton
- Currie (Edinburgh)
- Dalkeith
- Fala and Soutra
- Glencorse
- Heriot (Scottish Borders)
- Inveresk (East Lothian)
- Kirkliston (Edinburgh)[22]
- Kirknewton (West Lothian)
- Lasswade
- Mid Calder (West Lothian)
- Newbattle
- Newton
- Penicuik
- Ratho (Edinburgh)
- Stow (Scottish Borders)
- Temple
- West Calder (West Lothian)
Former civil parishes outside Edinburgh now merged in the City of Edinburgh
[edit]Abolished 1902:[23]
Abolished 1920[24]
The above list does not include parishes which have been within the City of Edinburgh for county purposes since 19th century, namely within the "County of the City" of which the Lord Provost was and is Lord Lieutenant.[25]
Transport
[edit]Midlothian has a modern road network as well as some rural single-track roads. The Borders Railway runs between Tweedbank to Edinburgh, with four stations in Midlothian – Shawfair, Eskbank, Newtongrange and Gorebridge.
Notable people associated with Midlothian
[edit]- William Drummond of Hawthornden (1585–1649), Scottish poet.
- Princess Margaret of Scotland (1598–1600), daughter of James VI and I of Scotland and England (born Dalkeith Palace)
- John Clerk of Penicuik, 2nd Baronet (1676–1755), was a Scottish politician, lawyer, judge, composer and architect.
- William Robertson (1721–1793), historian, minister in the Church of Scotland, and Principal of the University of Edinburgh
- Robert Smith (1722–1777), American architect, based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, born in Dalkeith
- Hector Macneill (1746–1818), poet and songwriter, born near Roslin
- John Clerk, Lord Eldin (1757–1832), Scottish judge, lived in Lasswade for several years.
- Sir Walter Scott (1771–1832) wrote the novel The Heart of Midlothian and lived at Lasswade Cottage (now Sir Walter Scott's Cottage) in Lasswade from 1798 to 1804, where he wrote his Grey Brother, translation of Goetz von Berlichingen, etc. and was visited by Wordsworth.
- William Tennant (1784–1848), the author of Anster Fair, was parish schoolmaster in Lasswade from 1816 to 1819.
- Thomas de Quincey (1785–1859), author of Confessions of an English Opium-Eater (1822), lived in Man's Bush Cottage (now De Quincey Cottage), Polton, from 1840 until his death in 1859.
- Thomas Murray (1792–1872), the Gallovidian author, died in Lasswade.
- Anne Richelieu Lamb (1807–1878), feminist writer
- William Ewart Gladstone (1809–1898), MP for Midlothian 1880–1895 and conducted his famous Midlothian campaign across the UK in 1880
- Patrick Edward Dove (1815–1873), mainly remembered for his book The Theory of Human Progression, born at Lasswade
- John Lawson Johnston (1839–1900), the creator of Bovril, born at Roslin.
- Charles W. Nibley (1849–1931), Scottish-American religious leader in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). Nibley was served as second counselor in the First Presidency to Heber J. Grant (1925–31), and Presiding Bishop (1907–25).
- Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869–1959) of Glencorse, Nobel prize-winning physicist.
- George Forrest (1873–1932), a plant collector who gained fame with his expeditions to the far east who spent a significant part of his early years in Loanhead.
- Sir William MacTaggart (1903–1981), artist, and grandson of the artist William McTaggart, he became President of the Society of Scottish Artists, President of the Royal Scottish Academy, and Trustee of the National Museum of Antiquities.
- Charles Forte, Baron Forte (1908–2007), the hotelier, worked in an Italian cafe in Loanhead, on his arrival in Scotland from Italy.
- Karl Miller (1931–2014), founding editor of the London Review of Books and Lord Northcliffe Professor of Modern English Literature at University College, London (1974–1992), born in Straiton.
- Annette Crosbie (born 1934), actress, born in Gorebridge
- Ishbel MacAskill (1941–2011), heritage activist and traditional Scottish Gaelic singer and teacher
- Fish (singer) (born 1958), former lead singer Marillion 1981-1987 and song based on his birth county, Heart of Midlothian (Royal Mile)
- Gary Naysmith from Loanhead (born 1978), Scottish International Footballer who played for Heart of Midlothian and Everton. He was named Scottish PFA Young Player of the Year in 1998. He won the Scottish Cup with Hearts in 1998.
- Darren Fletcher (born 1984), from Mayfield Dalkeith. Scotland International footballer and holds the record of being the youngest player to captain his national side, and was part of the Manchester United squad that won the UEFA Champions League in the 2007–2008 season.
- Steven Whittaker from Bonnyrigg, (born 1984), Scotland International footballer, ex-Hibernian F.C. and Rangers F.C.
Schools in Midlothian
[edit]Primary schools
[edit]- Bilston Primary School, Bilston
- Bonnyrigg Primary School, Bonnyrigg
- Burnbrae Primary School, Hopefield
- Cornbank St James Primary School, Penicuik
- Cuiken Primary School, Penicuik
- Danderhall Primary School, Danderhall
- Gore Glen Primary School, Gorebridge
- Gorebridge Primary School, Gorebridge
- Hawthornden Primary School, Bonnyrigg
- King's Park Primary School, Dalkeith
- Lasswade Primary School, Lasswade
- Lawfield Primary School, Mayfield
- Loanhead Primary School, Loanhead
- Mauricewood Primary School, Penicuik
- Mayfield Primary School, Mayfield
- Moorfoot Primary School, North Middleton
- Newtongrange Primary School, Newtongrange
- Paradykes Primary School, Loanhead
- Rosewell Primary School, Rosewell
- Roslin Primary School, Roslin
- Sacred Heart RC Primary School, Penicuik
- St Andrews's RC Primary School Gorebridge
- St David's RC Primary School Dalkeith
- St Luke's RC Primary School, Mayfield
- St Margaret's RC Primary School, Loanhead
- St Mary's RC Primary School, Bonnyrigg
- St Matthew's RC Primary School, Rosewell
- Stobhill Primary School, Gorebridge
- Strathesk Primary School, Penicuik
- Tynewater Primary School, Pathhead
- Woodburn Primary School, Woodburn
Secondary schools
[edit]- Beeslack High School, Penicuik
- Dalkeith High School, Dalkeith
- Lasswade High School Centre, Bonnyrigg
- Newbattle Community High School, Mayfield
- Penicuik High School, Penicuik
- St. David's RC High School, Dalkeith
Special schools
[edit]- Saltersgate School, Dalkeith
- Top Services Pathhead
Twin towns and sister cities
[edit]Midlothian is twinned with Komárom-Esztergom, Hungary and Kreis Heinsberg, Germany. It is a sister city with Midlothian, Illinois, a suburb of Chicago a town of Illinois.[26]
References
[edit]- ^ "The History of Dalkeith House and Estate" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 January 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2011.
- ^ "The History of Dalkeith House and Estate" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 January 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2011.
- ^ Chalmers, George (1889). "Edinburghshire: Of its establishment as a shire". Caledonia. Paisley: Alexander Gardner. pp. 559, 574, 579. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ Brown, Keith. "Act of the convention of estates of the kingdom of Scotland etc. for a new and voluntary offer to his majesty of £72,000 monthly for the space of twelve months, 23 January 1667". Records of the Parliament of Scotland. University of St Andrews. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 (52 & 53 Vict. c. 50)
- ^ "County councils: Mid-Lothian". Edinburgh Evening News. 13 February 1890. p. 3. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "Mid-Lothian County Council: Preserving an old name". Edinburgh Evening News. 12 March 1913. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "Imperial Parliament: House of Commons, Tuesday, June 3 - "Mid-Lothian" or "Edinburgh"". The Scotsman. Edinburgh. 4 June 1913. p. 9. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "Local Government (Scotland) Act 1947", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, 1947 c. 43, retrieved 24 December 2022
- ^ Historic Environment Scotland. "59-63 George IV Bridge, Lothian Chambers, including boundary balustrade (LB27674)". Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ "Land Mass Coverage Report" (PDF). Registers of Scotland. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- ^ "Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, 1973 c. 65, retrieved 24 December 2022
- ^ "Boundaries viewer". National Library of Scotland. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "The Lord-Lieutenants Order 1975", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 1975/428, retrieved 27 November 2022
- ^ "No. 19730". The Edinburgh Gazette. 2 September 1975. p. 1163.
- ^ "Remember when". Edinburgh Evening News. 7 September 2016. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, 1994 c. 39, retrieved 16 December 2022
- ^ "The Lord-Lieutenants (Scotland) Order 1996", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 1996/731, retrieved 16 December 2022
- ^ "Mid-2020 Population Estimates for Settlements and Localities in Scotland". National Records of Scotland. 31 March 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- ^ List from Contents page of the Statistical Account of Edinburghshire, published by William Blackwood and Sons, Edinburgh, 1845, including only those parishes appearing in the 2011 Census
- ^ Census of Scotland 2011, Table KS101SC – Usually Resident Population, published by National Records of Scotland. Website http://www.scotlandscensus.gov.uk/ retrieved March 2016. See "Standard Outputs", Table KS101SC, Area type: Civil Parish 1930
- ^ Partly in West Lothian. Article on Kirkliston in Ordnance Gazetteer of Scotland, by, Francis Groome, 2nd Edition, 1896
- ^ Order of the Secretary State for Scotland, effective from 15 May 1902, publ. in Edinburgh Gazette 1 April 1902, p. 350
- ^ Edinburgh Boundaries Extension and Tramways Act 1920 (10 & 11 Geo. 5. c. lxxxvii)
- ^ The Statistical Account of Edinburghshire, publ by William Blackwood and Sons, Edinburgh, 1845;p.648
- ^ "Illinois Member List updated June 2015 »". www.illinoissistercities.org. Retrieved 29 March 2018.
External links
[edit] Media related to Midlothian at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Midlothian at Wikimedia Commons