Allium cernuum
| Nodding onion | |
|---|---|

| |
| Umbel | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Amaryllidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Allioideae |
| Genus: | Allium |
| Species: | A. cernuum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Allium cernuum | |
| Synonyms[2][3] | |
| |
Allium cernuum, known as nodding onion or lady's leek,[4] is a perennial plant in the genus Allium. It grows in open areas in North America.
Description
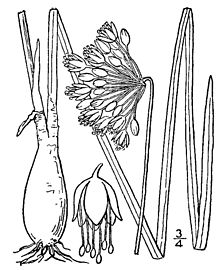
[edit]Allium cernuum is a herbaceous perennial growing from an unsheathed elongated conical bulb which gradually tapers directly into several keeled (thin and flat) grass-like leaves, 2–4 millimetres (3⁄32–5⁄32 inch) in width. Each mature bulb bears a single flowering stem, which terminates in a downward nodding umbel of white or rose, campanulate (bell-shaped) flowers that bloom in July and August. The flowers are arranged into downward facing umbels and each flower is about 5 mm (3⁄16 in) across, pink or white with yellow pollen and yellow anthers. A. cernuum does not have bulblets in the inflorescence.[5] The flowers mature into spherical crested fruits which later split open to reveal the dark shiny seeds.[6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13]
-
1913 illustration
-
Plant in New Mexico
-
Flowers in bloom
-
White flowers
-
Seed head
Similar species
[edit]In addition to other species of Allium, wild garlic, field garlic, and wild leek look similar,[14] as well as other onion-looking poisonous species, such as deathcamas, which lacks the expected onion odor.[14]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]
The species has been reported from much of the United States, Canada and Mexico including in the Appalachian Mountains from Alabama to New York State, the Great Lakes Region, the Ohio and Tennessee River Valleys, the Ozarks of Arkansas and Missouri, and the Rocky and Cascade Mountains of the West, from Mexico to Washington. It has not been reported from California, Nevada, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, New Jersey, Delaware, New England, or much of the Great Plains. In Canada, it grows from Ontario to British Columbia.[6][15][16][17][18]
Despite its wide geographical distribution, it is absent from much of its range. In the southern part of its range in North America it is limited to mountainous habitats, and in other parts of its North American range it is limited to local and disjunct population. It is absent from North Dakota and most of the Great Plains states and intermountain region of the U.S.[5] In Minnesota it is listed as a threatened species.[19]
It can be found growing in deciduous woodlands, to open grasslands.[5]
Uses
[edit]While A. cernuum is edible and has a strong onion flavor, it is not considered to have culinary value in the modern world.[20]
Cultivation
[edit]It is grown in gardens for its distinctive nodding flowers that are white, pink, or maroon; it is winter hardy in U.S. Department of Agriculture hardiness zones 3–9.[4] In gardens it will often form dense clusters of bulbs over time from offsets of the parent bulb.[21] Plants are healthiest in full sun with well drained soil, though in hot climates they appreciate some shade especially in the afternoons.[20]
References
[edit]- ^ NatureServe (2023). "Allium cernuum Nodding Onion". NatureServe Explorer. Arlington, Virginia: NatureServe. Retrieved 17 April 2023.
- ^ "Allium cernuum". Tropicos. Missouri Botanical Garden.
- ^ "Allium cernuum". World Checklist of Selected Plant Families. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew – via The Plant List. Note that this website has been superseded by World Flora Online
- ^ a b Geoffrey Burnie (1999). Botanica: The Illustrated A-Z of Over 10,000 Garden Plants. Welcome Rain. p. 75. ISBN 0760716420.
- ^ a b c Barbara Coffin; Lee Pfannmuller (1988). Minnesota's Endangered Flora and Fauna. U of Minnesota Press. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-8166-1689-3.
- ^ a b McNeal Jr., Dale W.; Jacobsen, T. D. (2002). "Allium cernuum". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). Vol. 26. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- ^ Hilty, John (2020). "Nodding Onion (Allium cernuum)". Illinois Wildflowers. Retrieved 24 June 2023.
- ^ Gleason, H. A.; Cronquist, A.J. (1991). Manual of the Vascular Plants of Northeastern United States and Adjacent Canada (2 ed.). Bronx: New York Botanical Garden. pp. i–910.
- ^ Cronquist, A.J.; Holmgren, A. H.; Holmgren, N. H.; Reveal, J. L. (1977). "Vascular Plants of the Intermountain West, U.S.A.". In Cronquist, A.J.; Holmgren, A. H.; Holmgren, N. H.; Reveal, J. L.; Holmgren, P. K. (eds.). Intermountain Flora. Vol. 6. New York: Hafner Pub. Co. pp. 1–584.
- ^ Hitchcock, C. H.; Cronquist, A.J.; Ownbey, F. M.; Thompson, J. W. (1969). "Vascular Cryptogams, Gymnosperms, and Monocotyledons". In Hitchcock, C. L. (ed.). Vascular Plants of the Pacific Northwest. Vol. 1. Seattle: University of Washington Press. pp. 1–914.
- ^ Radford, A. E.; Ahles, H. E.; Bell, C. R. (1968). Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. pp. i–lxi, 1–1183.
- ^ Moss, E. H. (1983). Flora of Alberta (2 ed.). Toronto: University of Toronto Press. pp. i–xii, 1–687. ISBN 9780802025081.
- ^ Bailey, L.H.; Bailey, E.Z. (1976). Hortus Third. New York: MacMillan. p. 49. ISBN 9780025054707.
- ^ a b Elias, Thomas S.; Dykeman, Peter A. (2009) [1982]. Edible Wild Plants: A North American Field Guide to Over 200 Natural Foods. New York: Sterling. p. 58. ISBN 978-1-4027-6715-9. OCLC 244766414.
- ^ "Allium cernuum". County-level distribution map from the North American Plant Atlas (NAPA). Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2014.
- ^ USDA, NRCS (n.d.). "Allium cernuum". The PLANTS Database (plants.usda.gov). Greensboro, North Carolina: National Plant Data Team.
- ^ Brako, L.; Rossman, A.Y.; Farr, D.F. (1995). Scientific and Common Names of 7,000 Vascular Plants in the United States. pp. 1–294.
- ^ CONABIO. 2009. Catálogo taxonómico de especies de México. 1. In Capital Nat. México. CONABIO, Mexico City.
- ^ "Endangered, Threatened, and Special Concern. Species ID Guide" (PDF). Minnesota Landscape Arboretum.
- ^ a b "Allium cernuum". Missouri Botanical Garden Plant Finder. Missouri Botanical Garden. Retrieved 2 June 2023.
- ^ Barr, Claude A. (1983). Jewels of the plains : wild flowers of the Great Plains grasslands and hills. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. p. 19. ISBN 0-8166-1127-0.
External links
[edit] Media related to Allium cernuum at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Allium cernuum at Wikimedia Commons- "Allium cernuum". Plants for a Future.