Vidin
Vidin
Видин (Bulgarian) | |
|---|---|
Vidin | |
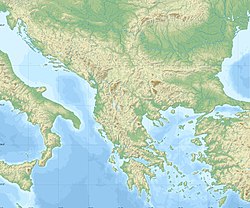
 Location of Vidin Province in Bulgaria | |
| Coordinates: 43°59′35″N 22°52′20″E / 43.99306°N 22.87222°E | |
| Country | Bulgaria |
| Province (Oblast) | Vidin |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Tsvetan Tsenkov |
| Area | |
• City | 63.218 km2 (24.409 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 34 m (112 ft) |
| Population (2022)[1] | |
• City | 34,797 |
| • Urban | 46,269 |
| Demonym | Vidinite |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal Code | 3700 |
| Area code | 094 |
| Website | vidin.bg |
 | |
Vidin (Bulgarian: Видин, pronounced [ˈvidin]) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as of the Metropolitan of Vidin (since 870).
An industrial, agricultural, and trade centre, Vidin has a fertile hinterland renowned for its wines.
Name
[edit]The name is archaically spelled as Widdin in English. Its older form Dunonia meant "fortified hill" in Celtic with the dun element found frequently in Celtic place names.[2] It is known as Diiu in Romanian.
Geography
[edit]Vidin is the westernmost important Bulgarian Danube port and is situated on one of the southernmost sections of the river. The New Europe Bridge, completed in 2013, connects Vidin to the Romanian town of Calafat on the opposite bank of the Danube. Previously, a ferry located 2 km (1 mi) from the town was in use for that purpose.
History
[edit]Vidin emerged at the place of an old Celtic settlement known as Dunonia.
The Romans built a fort here (called Bononia) on the Danubian Limes frontier system along the Danube and around which a Roman town developed. The town grew into one of the important centres of the province of Upper Moesia, encompassing the territory of modern north-western Bulgaria and eastern Serbia.
Middle Ages
[edit]
When Slavs settled in the area, they called the town Badin or Bdin, where the modern name comes from. Similarly, Anna Komnene refers to it as Vidynē (Βιδύνη) in the Alexiad. Vidin's main landmark, the Baba Vida fortress, was built in the period from the 10th to the 14th century. In the Middle Ages Vidin used to be an important Bulgarian city, a bishop seat and capital of a large province of the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018). Between 971 and 976 the town was the center of future Bulgarian emperor Samuil's possessions while his brothers ruled to the south. In 1003 Vidin was seized by Basil II after an eight-month siege because of the betrayal of the local bishop. Its importance once again rose during the Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1422) and its despots were influential figures in the Empire and were on several occasions chosen for emperors. From the mid 13th century it was ruled by the Shishman dynasty.
By early 1290s the Kingdom of Serbia expanded towards the vicinity of Vidin, after defeating the Bulgarian rulers of the region of Braničevo, Darman and Kudelin. Threatened by Serbian expansion, the Bulgarian despot Shishman of Vidin failed to repel the Serb forces, and accepted Serbian suzerainty,[3] although in practice, Shishman continued to be independent from Serbian influence and dealt mainly with Bulgaria.[4] Formal Serbian suzerainty lasted until Serbian king Stefan Milutin´s death, in 1321. As Milutin left no testament, after his death, in Serbia occurred a period of civil war with Stefan Dečanski, Stefan Konstantin and Stefan Vladislav II fighting for power. Michael Shishman took advantage of this situation, set free from Serbian overlordship, and returned to the Bulgarian sphere and in 1323 was chosen to be the Bulgarian emperor (tsar). After the death of Michael Shishman in the disastrous battle of Velbazhd in 1330, Vidin passed under the rule of his brother Belaur, who led un unsuccessful rebellion against the new emperor Ivan Alexander of Bulgaria (r. 1331–1371) until his defeat in 1336. In 1356 Ivan Alexander appointed his son Ivan Stratsimir (r. 1356–1396) as a ruler of Vidin, who governed the city and the surrounding region, the Tsardom of Vidin, as a de facto independent monarch.
Hungarian occupation of Vidin
[edit]In 1365, the Tsardom of Vidin was occupied by Magyar crusaders. Under Hungarian rule, the city became known as Bodony, but the occupation was short-lived. In 1369, the Bulgarian Empire drove out the Hungarian military, but in 1396 Vidin was occupied by a foreign force again this time being the Ottoman Empire under Bayezid I after the Battle of Nicopolis.
Ottoman rule
[edit]The Ottomans went on to conquer the despotates of Dobrudzha, Prilep and Velbazhd as well. Vidin's independence did not last long. In 1396, the Ottomans invaded and turned Vidin into a sandjak.[5]
The city fell under Austrian occupation in October 1689 during the Great Turkish War. Both Austrians and the Ottomans had heavy casualties during the siege. The occupation lasted nine months and ended in August 1690. Shortly after Vidin's capture, in 19 October 1689 2.500 Muslim men and 1,000 Muslim women from Vidin were deported to Nikopol. The Austrians also built a military facility in front of the Vidin citadel, where they placed more than 40 cannons. During the construction, a large number of Muslim houses and shops were destroyed. Of 3,000 buildings, two hammams, many mosques, shops and coffee shops only 200-300 buildings and several shops survived.[6]
In the late years of Ottoman rule, Vidin was the centre of Ottoman rebel Osman Pazvantoğlu's breakaway state.
In 1853, The Times of London reported that Widdin, as it was called, was
a considerable town, with a population of about 26,000, and a garrison of 8,000 to 10,000 men. Widdin is one of the important fortified places of the military line of the Danube. It covers the approaches of Servia, commands Little Wallachia, the defiles of Transylvania, and, above all, the opening of the road which leads through Nissia and Sophia on to Adrianople. Its form is an irregular pentagon; it is strongly bastioned, possesses a fortified castle, with two redoubts in the islands, and its defences are completed by an extensive marsh.[7]
In 1859 the English traveler Samuel Baker happened to visit Vidin and spotted the 14-year old Florence Barbara Maria von Sass from Transylvania (then in Hungary now in Romania) being sold into slavery, by some accounts destined to be owned by the Pasha of Vidin. Baker bribed her guards and took her with him, she eventually became Florence Baker, his wife and partner in the exploration of Africa .[8][5]
Some Muslims from Belgrade, Kladovo, and Smederevo settled in Vidin due to their expulsion from Serbia in 1862.[9]
Third Bulgarian State
[edit]After the Liberation of Bulgaria in 1878 Vidin was included in the reestablished Bulgarian state, the Principality of Bulgaria. The city was unsuccessfully besieged by the Serbian army during the Serbo-Bulgarian War in 1885 and the Second Balkan War in 1913.
Population
[edit]Vidin is the 20th town by population in Bulgaria, but serious demographic problems have been experienced in the area during the last two decades. The number of the residents of the city reached its peak between 1988 and 1991 when the population exceeded 65,000.[10] As of 2011, the town had a population of 48,071 inhabitants[11] and 35,784 inhabitants as of 2021.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1887 | 14,772 | — |
| 1910 | 16,450 | +11.4% |
| 1934 | 18,465 | +12.2% |
| 1946 | 18,481 | +0.1% |
| 1956 | 23,932 | +29.5% |
| 1965 | 36,835 | +53.9% |
| 1975 | 53,091 | +44.1% |
| 1985 | 62,693 | +18.1% |
| 1992 | 62,691 | −0.0% |
| 2001 | 57,395 | −8.4% |
| 2011 | 48,071 | −16.2% |
| 2021 | 39,568 | −17.7% |
| 2022 | 38,669 | −2.3% |
| Source: Censuses[12][13][14] | ||
Ethnic, linguistic and religious composition
[edit]According to the latest 2011 census data, the individuals declared their ethnic identity were distributed as follows:[15][16]
- Bulgarians: 40,550 (91.8%)
- Roma: 3,335 (7.5%)
- Turks: 60 (0.1%)
- Others: 199 (0.4%)
- Indefinable: 280 (0.6%)
- Undeclared: 3,647 (7.6%)
Total: 48,071
Climate
[edit]Vidin has a humid subtropical climate close to a temperate continental climate, from which it is shifting further and further away due to global warming. In the winter months, inversions are very common[citation needed]. The average annual temperature is 11.8 °C (53.2 °F).
| Climate data for Vidin, Bulgaria (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 21.7 (71.1) |
24.4 (75.9) |
28.0 (82.4) |
32.4 (90.3) |
35.4 (95.7) |
41.2 (106.2) |
43.6 (110.5) |
40.2 (104.4) |
36.4 (97.5) |
31.2 (88.2) |
26.4 (79.5) |
21.4 (70.5) |
43.6 (110.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 4.4 (39.9) |
7.2 (45.0) |
13.3 (55.9) |
19.2 (66.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.0 (87.8) |
25.2 (77.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
10.4 (50.7) |
5.0 (41.0) |
18.2 (64.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −0.2 (31.6) |
1.7 (35.1) |
6.6 (43.9) |
12.4 (54.3) |
17.7 (63.9) |
21.8 (71.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.0 (73.4) |
17.4 (63.3) |
11.4 (52.5) |
5.7 (42.3) |
0.8 (33.4) |
11.8 (53.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −3.9 (25.0) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
1.3 (34.3) |
5.8 (42.4) |
11.1 (52.0) |
14.8 (58.6) |
16.4 (61.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
11.5 (52.7) |
6.5 (43.7) |
2.0 (35.6) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
6.3 (43.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −24.0 (−11.2) |
−28.6 (−19.5) |
−13.6 (7.5) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
2.8 (37.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
7.0 (44.6) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−16.4 (2.5) |
−21.4 (−6.5) |
−28.6 (−19.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 41 (1.6) |
40 (1.6) |
43 (1.7) |
44 (1.7) |
56 (2.2) |
51 (2.0) |
55 (2.2) |
44 (1.7) |
44 (1.7) |
51 (2.0) |
46 (1.8) |
50 (2.0) |
565 (22.2) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0mm) | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 76 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 82 | 112 | 168 | 209 | 256 | 292 | 325 | 306 | 218 | 153 | 79 | 69 | 2,269 |
| Source: NOAA NCEI[17] | |||||||||||||
Tourism
[edit]
Vidin maintains two well-preserved medieval fortresses, Baba Vida and Kaleto, as well as many old Orthodox churches such as St Pantaleimon, St Petka (both 17th century), and St Dimitar (Demetrius of Thessaloniki) (19th century), the Vidin Synagogue (1894), the Osman Pazvantoğlu Mosque and library, the late 18th-century Turkish ruler of north-western Bulgaria, the Krastata Kazarma of 1798, and a number of old Renaissance buildings. Also remarkable is the theatre building which was the first Bulgarian theatre in "European model" and was built in 1891. The Vidin Synagogue built in 1894 was in 2021 a shell of its former self; plans are made to turn it into an interfaith cultural center; the Jews of Vidin number about a dozen.[18]
Another tourist attraction in the Vidin area is the town of Belogradchik, famous for its unique and impressive rock formations, the Belogradchik Rocks and the medieval Belogradchik Fortress and also the nearby Magura Cave with its beautiful prehistoric cave paintings.
Archaeology
[edit]A fragmented marble structure found near Vidin shows a bearded man in a Phrygian cap and Roman armor, identified as Jupiter Dolichenus, holding a thunderbolt and likely a bipennis. This piece, dating from the late 2nd or early 3rd century, aligns with similar depictions of the deity found in other regions, suggesting a common iconographic theme.[19]
Transportation
[edit]
In Vidin is a border-station to neighbouring Romania via the Danube river. It was operated by ferryboats only until 14 June 2013 when the Vidin–Calafat Bridge opened. Crossing by ferry was possible only every 1⁄2 hour with just five trucks per ferry. Ticket prices were €50 per truck and €12 per car.
The city has a regional airport (Vidin Airport, ICAO code LBVD) a few kilometres to the north-west; as of 2000[update], there is no scheduled passenger service, and the buildings are in a state of disrepair. There are, however, state development plans to rebuild and restore the activity of Vidin airport.[20][21]
Landmarks
[edit]Close to the town lies a powerful medium wave broadcasting station (since 1973) whose signals can be easily received throughout Europe. It works on 576 khz with a power of 500 kW. For transmission on 576 kHz a 259-metre-tall (850 ft) guyed mast equipped with a cage antenna at its lower part is used. A powerful FM transmitter on 88.2 MHz provides good coverage for Hristo Botev radio. Also, Horizont and Radio Vidin are broadcast on 102.3 and 103.9 MHz with similar coverage to Hristo Botev
Honour
[edit]Vidin Heights on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica is named after Vidin.
Gallery
[edit]-
A view of the Danube from Baba Vida
-
Fin-de-siècle house
-
"Konaka"-Museum in an 18th-century building
-
Old building, previously used as a public bath
-
Osman Pazvantoğlu library
-
The art gallery
-
An old house
-
Stambol Kapiya
International relations
[edit]Twin towns — sister cities
[edit] Calafat, Romania
Calafat, Romania Demre, Turkey
Demre, Turkey Hódmezővásárhely, Hungary
Hódmezővásárhely, Hungary Rivne, Ukraine
Rivne, Ukraine West Carrollton, United States
West Carrollton, United States Zaječar, Serbia
Zaječar, Serbia
Partner towns
[edit]Partner towns of Vidin:[22]
 Debar, North Macedonia
Debar, North Macedonia Deggendorf, Germany
Deggendorf, Germany Lecco, Italy
Lecco, Italy Ulm, Germany
Ulm, Germany
Consulate
[edit]- Honorary Consulate of Romania
Sports
[edit]
The football team of the town (FC Bdin) was established in 1923.
References
[edit]- ^ НАСЕЛЕНИЕ КЪМ 31.12.2022 Г. ПО ОБЛАСТИ, ОБЩИНИ, МЕСТОЖИВЕЕНЕ И ПОЛ nsi.bg
- ^ Veyrenc, Charles Jacques (1981). Bulgaria Nagel's encyclopedia-guide (2 ed.). Nagel. p. 413. ISBN 978-2-8263-0560-6.
In the 3rd century BC the Celts established on the site now occupied by Vidin a fortress to which they gave the name of Dunonia, "fortified hill"
- ^ The Balkans: From Constantinople to Communism by D. Hupchick, page 88
- ^ Андреев, Йордан; Лазаров, Иван; Павлов, Пламен (1999). Кой кой е в средновековна България [Who is Who in Medieval Bulgaria] (in Bulgarian). Петър Берон. p. 395. ISBN 978-954-402-047-7.
- ^ a b Science historian chronicles true story of Lady Florence Baker, Penn State University, 3 February 2004, Retrieved 4 September 2015
- ^ Todorova, Olga. An episode from the History of Vidin (1689/1690): Some reflections on Hristo Gandev's theory of the so-called "Bulgarization" of towns, p. 108-109
- ^ "The Seat of War on the Danube," The Times, December 29, p. 8
- ^ Dorothy Middleton, 'Baker, Florence Barbara Maria, Lady Baker (1841–1916)', Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 2004 accessed 5 Sept 2015
- ^ Özkan, Ayşe (January 2011). "The Expulsion of Muslims from Serbia after the International Conference in Kanlıca and Withdrawal of the Ottoman Empire from Serbia (1862-1867)". Akademik Bakış. 5 (9): 123–138.
- ^ "CDS/ISIS on the Web - Navigator". Archived from the original on 2014-08-19. Retrieved 2022-03-08.
- ^ "ПРЕБРОЯВАНЕ 2011" (PDF). Nsi.bg. Retrieved 15 October 2017.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-06. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Cities of Bulgaria". 2024-04-03.
- ^ "Sational statistical institute". 2024-10-31.
- ^ "Population on 01.02.2011 by provinces, municipalities, settlements and age" (XLS). Bulgarian National Statistical Institute. Retrieved 15 October 2017.
- ^ "Population by province, municipality, settlement and ethnic identification" (XLS). Bulgarian National Statistical Institute. Retrieved 15 October 2017.
- ^ "Climate normals for 1991-2020: Vidin" (CSV). Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ Kay, Jonah Goldman. "Abandoned Bulgarian synagogue to become cultural center and interfaith hub". www.timesofisrael.com.
- ^ Vitas, Nadežda Gavrilović (2021). Ex Asia et Syria: Oriental Religions in the Roman Central Balkans. Archaeopress. p. 101. doi:10.2307/j.ctv1gt94hj.12. JSTOR j.ctv1gt94hj.
- ^ Kostova, Anelia (2022-08-06). "Vidin airport near the village of Inovo will be rebuilt" (in Bulgarian). Darik. Retrieved 2023-02-21.
- ^ "Northwest Bulgaria's Authorities Seek Investors to Revive Vidin Airport". Novinite.com. 2011-08-11. Retrieved 2023-02-21.
- ^ a b "Международно сътрудничество". vidin.bg (in Bulgarian). Vidin. Retrieved 2019-10-31.
External links
[edit]- The Information Web Portal of Vidin Archived 2018-04-03 at the Wayback Machine
- Pictures Of Baba Vida
- Old Pictures From Vidin
- Vidin info
- Vidin article at Pictures of Bulgaria Archived 2012-02-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Vidin photo gallery Archived 2011-10-18 at the Wayback Machine
- Pictures of Vidin Broadcasting Station