Bessemer process

The Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation with air being blown through the molten iron. The oxidation also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten.
The modern process is named after its inventor, the Englishman Henry Bessemer, who took out a patent on the process in 1856.[1] The process was said to be independently discovered in 1851 by the American inventor William Kelly[2][3] though the claim is controversial.[4][5][6][7]
The process using a basic refractory lining is known as the "basic Bessemer process" or Gilchrist–Thomas process after the English discoverers Percy Gilchrist and Sidney Gilchrist Thomas.
History
[edit]
Early history
[edit]China
[edit]A system akin to the Bessemer process has existed since the 11th century in East Asia.[8][9] Economic historian Robert Hartwell writes that the Chinese of the Song dynasty (960–1279 CE) innovated a "partial decarbonization" method of repeated forging of cast iron under a cold blast.[10] Sinologist Joseph Needham and historian of metallurgy Theodore A. Wertime have described the method as a predecessor to the Bessemer process of making steel.[8][11][12] This process was first described by the prolific scholar and polymath government official Shen Kuo (1031–1095) in 1075, when he visited Cizhou.[10] Hartwell states that perhaps the earliest center where this was practiced was the great iron-production district along the Henan–Hebei border during the 11th century.[10]
Europe
[edit]In the 15th century, the finery process, another process which shares the air-blowing principle with the Bessemer process, was developed in Europe. In 1740, Benjamin Huntsman developed the crucible technique for steel manufacture, at his workshop in the district of Handsworth in Sheffield. This process had an enormous impact on the quantity and quality of steel production, but it was unrelated to the Bessemer-type process employing decarburization.

The Japanese may have made use of a Bessemer-type process, which was observed by European travellers in the 17th century.[2] The adventurer Johan Albrecht de Mandelslo describes the process in a book published in English in 1669. He writes, "They have, among others, particular invention for the melting of iron, without the using of fire, casting it into a tun done about on the inside without about half a foot of earth, where they keep it with continual blowing, take it out by ladles full, to give it what form they please." According to historian Donald Wagner, Mandelslo did not personally visit Japan, so his description of the process is likely derived from accounts of other Europeans who had traveled to Japan. Wagner believes that the Japanese process may have been similar to the Bessemer process, but cautions that alternative explanations are also plausible.[2]
Bessemer's patent
[edit]
In the early to mid-1850s, the American inventor William Kelly experimented with a method similar to the Bessemer process. Wagner writes that Kelly may have been inspired by techniques introduced by Chinese ironworkers hired by Kelly in 1854.[2] The claim that both Kelly and Bessemer invented the same process remains controversial. When Bessemer's patent for the process was reported by Scientific American, Kelly responded by writing a letter to the magazine. In the letter, Kelly states that he had previously experimented with the process and claimed that Bessemer knew of Kelly's discovery. He wrote that "I have reason to believe my discovery was known in England three or four years ago, as a number of English puddlers visited this place to see my new process. Several of them have since returned to England and may have spoken of my invention there."[2] It is suggested Kelly's process was less developed and less successful than Bessemer's process.[13]

Sir Henry Bessemer described the origin of his invention in his autobiography written in 1890. During the outbreak of the Crimean War, many English industrialists and inventors became interested in military technology. According to Bessemer, his invention was inspired by a conversation with Napoleon III in 1854 pertaining to the steel required for better artillery. Bessemer claimed that it "was the spark which kindled one of the greatest revolutions that the present century had to record, for during my solitary ride in a cab that night from Vincennes to Paris, I made up my mind to try what I could to improve the quality of iron in the manufacture of guns."[1] At the time, steel was used to make only small items like cutlery and tools, but was too expensive for cannons. Starting in January 1855, he began working on a way to produce steel in the massive quantities required for artillery and by October he filed his first patent related to the Bessemer process. He patented the method a year later in 1856.[1] William Kelley was awarded priority patent in 1857.[14]

Bessemer licensed the patent for his process to four ironmasters,[when?] for a total of £27,000, but the licensees failed to produce the quality of steel he had promised—it was "rotten hot and rotten cold", according to his friend, William Clay[15]—and he later bought them back for £32,500.[16] His plan had been to offer the licenses to one company in each of several geographic areas, at a royalty price per ton that included a lower rate on a proportion of their output in order to encourage production, but not so large a proportion that they might decide to reduce their selling prices. By this method he hoped to cause the new process to gain in standing and market share.[15]
He realised that the technical problem was due to impurities in the iron and concluded that the solution lay in knowing when to turn off the flow of air in his process so that the impurities were burned off but just the right amount of carbon remained. However, despite spending tens of thousands of pounds on experiments, he could not find the answer.[17] Certain grades of steel are sensitive to the 78% nitrogen which was part of the air blast passing through the steel.
The solution was first discovered by English metallurgist Robert Forester Mushet, who had carried out thousands of experiments in the Forest of Dean. His method was to first burn off, as far as possible, all the impurities and carbon, then reintroduce carbon and manganese by adding an exact amount of spiegeleisen, an alloy of iron and manganese with trace amounts of carbon and silicon. This had the effect of improving the quality of the finished product, increasing its malleability—its ability to withstand rolling and forging at high temperatures and making it more suitable for a vast array of uses.[18][19] Mushet's patent ultimately lapsed due to Mushet's inability to pay the patent fees and was acquired by Bessemer. Bessemer earned over 5 million dollars[clarification needed] in royalties from the patents.[20]
The first company to license the process was the Manchester firm of W & J Galloway, and they did so before Bessemer announced it at Cheltenham in 1856. They are not included in his list of the four to whom he refunded the license fees. However, they subsequently rescinded their license in 1858 in return for the opportunity to invest in a partnership with Bessemer and others. This partnership began to manufacture steel in Sheffield from 1858, initially using imported charcoal pig iron from Sweden. This was the first commercial production.[15][21]
A 20% share in the Bessemer patent was also purchased for use in Sweden and Norway by Swedish trader and Consul Göran Fredrik Göransson during a visit to London in 1857. During the first half of 1858, Göransson, together with a small group of engineers, experimented with the Bessemer process at Edsken near Hofors, Sweden before he finally succeeded. Later in 1858 he again met with Henry Bessemer in London, managed to convince him of his success with the process, and negotiated the right to sell his steel in England. Production continued in Edsken, but it was far too small for the industrial-scale production needed. In 1862 Göransson built a new factory for his Högbo Iron and Steel Works company on the shore of Lake Storsjön, where the town of Sandviken was founded. The company was renamed Sandviken's Ironworks, continued to grow and eventually became Sandvik in the 1970s.[22]
Industrial revolution in the United States
[edit]Alexander Lyman Holley contributed significantly to the success of Bessemer steel in the United States. His A Treatise on Ordnance and Armor[23] is an important work on contemporary weapons manufacturing and steel-making practices. In 1862, he visited Bessemer's Sheffield works, and became interested in licensing the process for use in the US. Upon returning to the US, Holley met with two iron producers from Troy, New York, John F. Winslow and John Augustus Griswold, who asked him to return to the United Kingdom and negotiate with the Bank of England on their behalf. Holley secured a license for Griswold and Winslow to use Bessemer's patented processes and returned to the United States in late 1863.[24]
The trio began setting up a mill in Troy, New York in 1865. The factory contained a number of Holley's innovations that greatly improved productivity over Bessemer's factory in Sheffield, and the owners gave a successful public exhibition in 1867. The Troy factory attracted the attention of the Pennsylvania Railroad, which wanted to use the new process to manufacture steel rail. It funded Holley's second mill as part of its Pennsylvania Steel subsidiary. Between 1866 and 1877, the partners were able to license a total of 11 Bessemer steel mills.
One of the investors they attracted was Andrew Carnegie, who saw great promise in the new steel technology after a visit to Bessemer in 1872, and saw it as a useful adjunct to his existing businesses, the Keystone Bridge Company and the Union Iron Works. Holley built the new steel mill for Carnegie, and continued to improve and refine the process. The new mill, known as the Edgar Thomson Steel Works, opened in 1875, and started the growth of the United States as a major world steel producer.[25] Using the Bessemer process, Carnegie Steel was able to reduce the costs of steel railroad rails from $100 per ton to $50 per ton between 1873 and 1875. The price of steel continued to fall until Carnegie was selling rails for $18 per ton by the 1890s. Prior to the opening of Carnegie's Thomson Works, steel output in the United States totaled around 157,000 tons per year. By 1910, American companies were producing 26 million tons of steel annually.[26]
William Walker Scranton, manager and owner of the Lackawanna Iron & Coal Company in Scranton, Pennsylvania, had also investigated the process in Europe. He built a mill in 1876 using the Bessemer process for steel rails and quadrupled his production.[27]
Bessemer steel was used in the United States primarily for railroad rails. During the construction of the Brooklyn Bridge, a major dispute arose over whether crucible steel should be used instead of the cheaper Bessemer steel. In 1877, Abram Hewitt wrote a letter urging against the use of Bessemer steel in the construction of the Brooklyn Bridge.[28][29] Bids had been submitted for both crucible steel and Bessemer steel; John A. Roebling's Sons submitted the lowest bid for Bessemer steel,[30] but at Hewitt's direction, the contract was awarded to J. Lloyd Haigh Co.[31]
Technical details
[edit]
Using the Bessemer process, it took between 10 and 20 minutes to convert three to five tons of iron into steel – it would previously take at least a full day of heating, stirring and reheating to achieve this.[26]
Oxidation
[edit]The blowing of air through the molten pig iron introduces oxygen into the melt which results in oxidation, removing impurities found in the pig iron, such as silicon, manganese, and carbon in the form of oxides. These oxides either escape as gas or form a solid slag. The refractory lining of the converter also plays a role in the conversion — clay linings may be used when there is little phosphorus in the raw material, and Bessemer himself used ganister sandstone – this is known as the acid Bessemer process. When the phosphorus content is high, dolomite, or sometimes magnesite, linings are required in the basic Bessemer limestone process, see below. In order to produce steel with desired properties, additives such as spiegeleisen (a ferromanganese alloy), can be added to the molten steel once the impurities have been removed.
Managing the process
[edit]When the required steel had been formed, it was poured into ladles and then transferred into moulds while the lighter slag was left behind. The conversion process, called the "blow", was completed in approximately 20 minutes. During this period, the progress of the oxidation of the impurities was judged by the appearance of the flame issuing from the mouth of the converter. The modern use of photoelectric methods of recording the characteristics of the flame greatly aided the blower in controlling final product quality. After the blow, the liquid metal was recarburized to the desired point and other alloying materials were added, depending on the desired product.
A Bessemer converter could treat a "heat" (batch of hot metal) of 5 to 30 tons at a time.[32] They were usually operated in pairs, one being blown while another was being filled or tapped.
Predecessor processes
[edit]
By the early 19th century the puddling process was widespread. Until technological advances made it possible to work at higher heats, slag impurities could not be removed entirely, but the reverberatory furnace made it possible to heat iron without placing it directly in the fire, offering some degree of protection from the impurity of the fuel source. Thus, with the advent of this technology, coal began to replace charcoal fuel. The Bessemer process allowed steel to be produced without fuel, using the impurities of the iron to create the necessary heat. This drastically reduced the costs of steel production, but raw materials with the required characteristics could be difficult to find.[33]
High-quality steel was made by the reverse process of adding carbon to carbon-free wrought iron, usually imported from Sweden. The manufacturing process, called the cementation process, consisted of heating bars of wrought iron together with charcoal for periods of up to a week in a long stone box. This produced blister steel. The blister steel was put in a crucible with wrought iron and melted, producing crucible steel. Up to 3 tons of expensive coke was burnt for each ton of steel produced. Such steel when rolled into bars was sold at £50 to £60 (approximately £3,390 to £4,070 in 2008)[34] a long ton. The most difficult and work-intensive part of the process, however, was the production of wrought iron done in finery forges in Sweden.
This process was refined in the 18th century with the introduction of Benjamin Huntsman's crucible steel-making techniques, which added an additional three hours firing time and required additional large quantities of coke. In making crucible steel, the blister steel bars were broken into pieces and melted in small crucibles, each containing 20 kg or so. This produced higher quality crucible steel but increased the cost. The Bessemer process reduced the time needed to make lower-grade steel to about half an hour while requiring only the coke needed initially to melt the pig iron. The earliest Bessemer converters produced steel for £7 a long ton, although it initially sold for around £40 a ton.
"Basic" vs. acidic Bessemer process
[edit]Sidney Gilchrist Thomas, a Londoner with a Welsh father, was an industrial chemist who decided to tackle the problem of phosphorus in iron, which resulted in the production of low grade steel. Believing that he had discovered a solution, he contacted his cousin, Percy Gilchrist, who was a chemist at the Blaenavon Ironworks. The manager at the time, Edward Martin, offered Sidney equipment for large-scale testing and helped him draw up a patent that was taken out in May 1878. Sidney Gilchrist Thomas's invention consisted of using dolomite or sometimes limestone linings for the Bessemer converter rather than clay, and it became known as the 'basic' Bessemer rather than the 'acid' Bessemer process. An additional advantage was that the processes formed more slag in the converter, and this could be recovered and used very profitably as a phosphate fertilizer.[35]
Importance
[edit]
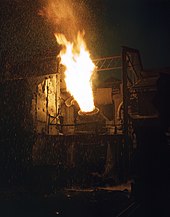
In 1898, Scientific American published an article called Bessemer Steel and its Effect on the World explaining the significant economic effects of the increased supply in cheap steel. They noted that the expansion of railroads into previously sparsely inhabited regions of the country had led to settlement in those regions, and had made the trade of certain goods profitable, which had previously been too costly to transport.[36]
The Bessemer process revolutionized steel manufacture by decreasing its cost, from £40 per long ton to £6–7 per long ton, along with greatly increasing the scale and speed of production of this vital raw material. The process also decreased the labor requirements for steel-making. Before it was introduced, steel was far too expensive to make bridges or the framework for buildings and thus wrought iron had been used throughout the Industrial Revolution. After the introduction of the Bessemer process, steel and wrought iron became similarly priced, and some users, primarily railroads, turned to steel. Quality problems, such as brittleness caused by nitrogen in the blowing air,[37] prevented Bessemer steel from being used for many structural applications.[38] Open-hearth steel was suitable for structural applications.
Steel greatly improved the productivity of railroads. Steel rails lasted ten times longer than iron rails. Steel rails, which became heavier as prices fell, could carry heavier locomotives, which could pull longer trains.[39] Steel rail cars were longer and were able to increase the freight to car weight from 1:1 to 2:1.
Obsolescence
[edit]As early as 1895 in the UK it was being noted that the heyday of the Bessemer process was over and that the open hearth method predominated. The Iron and Coal Trades Review said that it was "in a semi-moribund condition. Year after year, it has not only ceased to make progress, but it has absolutely declined." It has been suggested, both at that time and more recently, that the cause of this was the lack of trained personnel and investment in technology rather than anything intrinsic to the process itself.[40] For example, one of the major causes of the decline of the giant ironmaking company Bolckow Vaughan of Middlesbrough was its failure to upgrade its technology.[41] The basic process, the Thomas-Gilchrist process, remained in use longer, especially in Continental Europe, where iron ores were of high phosphorus content[42] and the open-hearth process was not able to remove all phosphorus; almost all inexpensive construction steel in Germany was produced with this method in the 1950s and 1960s.[43] It was eventually superseded by basic oxygen steelmaking.
In the U.S., commercial steel production using this method stopped in 1968. It was replaced by processes such as the basic oxygen (Linz–Donawitz) process, which offered better control of final chemistry. The Bessemer process was so fast (10–20 minutes for a heat) that it allowed little time for chemical analysis or adjustment of the alloying elements in the steel. Bessemer converters did not remove phosphorus efficiently from the molten steel; as low-phosphorus ores became more expensive, conversion costs increased. The process permitted only limited amount of scrap steel to be charged, further increasing costs, especially when scrap was inexpensive. Use of electric arc furnace technology competed favourably with the Bessemer process resulting in its obsolescence.
Basic oxygen steelmaking is essentially an improved version of the Bessemer process (decarburization by blowing oxygen as gas into the heat rather than burning the excess carbon away by adding oxygen carrying substances into the heat). The advantages of pure oxygen blast over air blast were known to Henry Bessemer,[citation needed] but 19th-century technology was not advanced enough to allow for the production of the large quantities of pure oxygen necessary to make it economical.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Wagner, Donald (2008). Science and Civilisation in China: Vol. 5, Part 11: Ferrous Metallurgy. Cambridge University Press. p. 361. ISBN 978-0-521-87566-0.
- ^ a b c d e f Wagner, Donald (2008). Science and Civilisation in China: Vol. 5, Part 11: Ferrous Metallurgy. Cambridge University Press. pp. 363–5. ISBN 978-0-521-87566-0.
- ^ "Bessemer process". Britannica. Vol. 2. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2005. p. 168.
- ^ Gordon, Robert B. (2001). American Iron, 1607–1900. JHU Press. pp. 221–. ISBN 978-0-8018-6816-0.
- ^ The Beginnings of Cheap Steel by Philip W. Bishop. Retrieved 23 February 2018 – via www.gutenberg.org.
- ^ "No. 762: Kelly's Converter". www.uh.edu. Retrieved 23 February 2018.
- ^ Shaping Technology/building Society: Studies in Sociotechnical Change. MIT Press. 29 September 1994. pp. 112–. ISBN 978-0-262-26043-5.
- ^ a b Needham, Joseph (2008). Science and civilisation in China, Volume 5, Part 7 (1. publ. ed.). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 261–5. ISBN 9780521875660.
- ^ Tanner, Harold (2009). China: A History. Hackett Publishing. p. 218. ISBN 978-0-87220-915-2.
- ^ a b c Hartwell, Robert (March 1966). "Markets, Technology, and the Structure of Enterprise in the Development of the Eleventh-Century Chinese Iron and Steel Industry". The Journal of Economic History. 26 (1): 54. doi:10.1017/S0022050700061842. ISSN 0022-0507. JSTOR 2116001. S2CID 154556274.
- ^ Wertime, Theodore A. (1962). The coming of the age of steel. University of Chicago Press.
- ^ Temple, Robert K.G. (1999). The Genius of China: 3000 years of science, discovery and invention. London: Prion. p. 49. ISBN 9781853752926.
- ^ "No. 762: Kelly's Converter".
- ^ "Kelly Pneumatic Iron Process". American Chemical Society. Retrieved 3 November 2023.
- ^ a b c Erickson, Charlotte (1986) [1959]. British industrialists: steel and hosiery 1850–1950. Cambridge University Press. pp. 141–142. ISBN 0-566-05141-9.
- ^ Bessemer, Sir Henry (1905). Sir Henry Bessemer, F.R.S. Offices of "Engineering". p172.
- ^ Anstis 1997, p. 147.
- ^ . Dictionary of National Biography. London: Smith, Elder & Co. 1885–1900.
- ^ Anstis 1997, p. 140.
- ^ Company, Lewis Publishing (1908). A century and a half of Pittsburg and her people. Lewis Pub. Co.
{{cite book}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Bessemer, Sir Henry (1905). An Autobiography. London: Engineering. pp. 176, 180.
- ^ "The Sandvik Journey : de första 150 åren - Ronald Fagerfjäll - inbunden (9789171261984) | Adlibris Bokhandel". www.adlibris.com. Retrieved 1 July 2020.
- ^ Holley, Alexander Lyman (1865). A Treatise on Ordnance and Armor. Trübner & company. Archived from the original on 27 June 2007.
- ^ Cutliffe, Stephen H. (1999). "Holley, Alexander Lyman". American National Biography (online ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/anb/9780198606697.article.1300778. (subscription required)
- ^ Thomas J. Misa, A Nation of Steel: The Making of Modern America, 1865–1925 (1995): chapter on Holley and Bessemer process online Archived 15 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Heilbroner, Robert L.; Singer, Aaron (1977). The economic transformation of America. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. ISBN 978-0-15-518800-6.
- ^ Cheryl A. Kashuba, "William Walker led industry in the city", The Times-Tribune, 11 July 2010, accessed 23 May 2016
- ^ "The Brooklyn Bridge". New York Daily Herald. 14 January 1877. p. 14. Retrieved 26 April 2018 – via newspapers.com
 .
.
- ^ McCullough, David (31 May 2007). The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn Bridge. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-0-7432-1831-3.
- ^ "Monthly Meeting of the Trustees". Brooklyn Daily Eagle. 12 January 1877. p. 2. Retrieved 26 April 2018 – via Brooklyn Public Library; newspapers.com
 .
.
- ^ Reier, Sharon (2012). Bridges of New York. Dover Publications. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-486-13705-6. OCLC 868273040.
- ^ "Bessemer Converter". www.steeltalk.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ Peter Temin (1963). "The Composition of Iron and Steel Products, 1869–1909". The Journal of Economic History. 23 (4): 447–471. doi:10.1017/S0022050700109179. JSTOR 2116209. S2CID 154397900.
- ^ "Purchasing Power of British Pounds from 1264 to Present". 2009. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- ^ Blaenavon World Heritage Site: Blaenavon and the 'Gilchrist-Thomas' Process Archived 12 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Bessemer Steel and its Effect on the World". Scientific American. 78 (13): 198. 1898. JSTOR 26116729.
- ^ Rosenberg, Nathan (1982). Inside the Black Box: Technology and Economics. Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 90. ISBN 0-521-27367-6.
- ^ Misa, Thomas J. (1999) [1995]. A Nation of Steel: The Making of Modern America, 1865–1925. Johns Hopkins studies in the history of technology. Baltimore, Md.: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-6052-0. OCLC 540692649. Chapter 1 online.
- ^ Rosenberg, Nathan (1982). Inside the Black Box: Technology and Economics. Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press. pp. 60, 69. ISBN 0-521-27367-6.
- ^ Payne, P. L. (1968). "Iron and steel manufactures". In Aldcroft, Derek H. (ed.). The development of British industry and foreign competition, 1875–1914; studies in industrial enterprise. London: George Allen & Unwin. pp. 92–94, 97. OCLC 224674.
- ^ Abe, E. The Technological Strategy of a Leading Iron and Steel Firm: Bolckow Vaughan Co. Ltd: Late Victorian Industrialists Did Fail. Business History, 1996, Vol. 38, No. 1, pages 45–76.
- ^ "Rail that Survived Demolition by "Lawrence of Arabia": An Analysis". www.tms.org. Archived from the original on 22 November 2017. Retrieved 23 February 2018.
- ^ "Thomas process / Metallurgy - Economy-point.org". Archived from the original on 3 February 2013. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
Bibliography
[edit]- Anstis, Ralph (1997), Man of Iron, Man of Steel: Lives of David and Robert Mushet, Albion House, ISBN 0-9511371-4-X
- Jackson, Albert (1964), Oxygen Steelmaking for Steelmakers, George Newnes Ltd., ISBN 978-0408073523
- Baggley, P.; Sanderson, N. (2002), A Pictorial archive of Steelmaking at Workington, ISBN 0-9538447-1-4
External links
[edit] "Progress in the Manufacture of Steel" in Popular Science Monthly Volume 19, October 1881
"Progress in the Manufacture of Steel" in Popular Science Monthly Volume 19, October 1881- "Bessemer's explanation of his process". The Engineer. 15 August 1856. Archived from the original on 28 October 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2011.
- "How the Modern Steel Furnace Does Its Work". Popular Science: 30–31. February 1919.

