Finnic languages
| Finnic | |
|---|---|
| Baltic Finnic, Balto-Finnic | |
| Geographic distribution | Fennoscandia, Estonia, Latvia, Northwestern Russia |
| Ethnicity | Balto-Finnic peoples |
| Linguistic classification | Uralic
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Finnic |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | finn1317 |
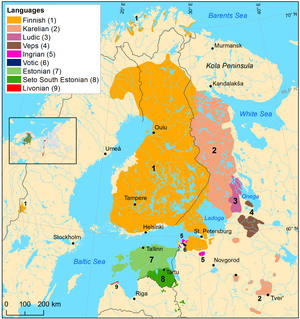 | |
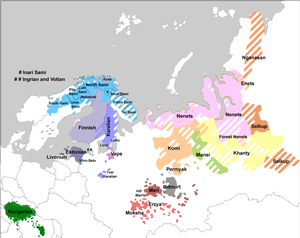
The Finnic or Baltic Finnic languages[a][4] constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia.
Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized.[5] The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.[6] The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian and Votic, spoken in Ingria by the Gulf of Finland, and Livonian, once spoken around the Gulf of Riga. Spoken farther northeast are Karelian, Ludic, and Veps, in the region of Lakes Onega and Ladoga.
In addition, since the 1990s, several Finnic-speaking minority groups have emerged to seek recognition for their languages as distinct from the ones they have been considered dialects of in the past. Some of these groups have established their own orthographies and standardised languages.[5] Võro and Seto, which are spoken in southeastern Estonia and in some parts of Russia, are considered dialects of Estonian by some linguists,[7] while other linguists consider them separate languages. Meänkieli and Kven are spoken in northern Sweden and Norway respectively and have the legal status of independent minority languages separate from Finnish. They were earlier considered dialects of Finnish and are mutually intelligible with it.[8] Additionally, the Karelian language was not officially recognised as its own language in Finland until 2009, despite there being no linguistic confusion about its status.
The smaller languages are endangered. The last native speaker of Livonian died in 2013, and only about a dozen native speakers of Votic remain. Regardless, even for these languages, the shaping of a standard language and education in it continues.[9]

The geographic centre of the maximum divergence between the languages is located east of the Gulf of Finland around Saint Petersburg. A glottochronological study estimates the age of the common ancestor of existing languages to a little more than 1000 years.[11] However, Mikko Heikkilä dates the beginning of the diversification (with South Estonian as the first split) rather precisely to about 150 AD, based on loanword evidence (and previous estimates tend to be even older, like Pekka Sammallahti's of 1000–600 BC). There is now wide agreement that Proto-Finnic was probably spoken at the coasts of the Gulf of Finland.[12]
Classification
[edit]The Finnic languages are located at the western end of the Uralic language family. A close affinity to their northern neighbors, the Sámi languages, has long been assumed, though many of the similarities (particularly lexical ones) can be shown to result from common influence from Germanic languages and, to a lesser extent, Baltic languages. Innovations are also shared between Finnic and the Mordvinic languages, and in recent times Finnic, Sámi and Moksha are sometimes grouped together.[13]
General characteristics
[edit]There is no grammatical gender in any of the Finnic languages, nor are there articles or definite or indefinite forms.[14]
The morphophonology (the way the grammatical function of a morpheme affects its production) is complex. Morphological elements found in the Finnic languages include grammatical case suffixes, verb tempus, mood and person markers (singular and plural, the Finnic languages do not have dual) as well as participles and several infinitive forms, possessive suffixes, clitics and more. The number of grammatical cases tends to be high while the number of verb infinitive forms varies more by language.
One of the more important processes is the characteristic consonant gradation. Two kinds of gradation occur: radical gradation and suffix gradation. They both affect the plosives /k/, /t/ and /p/,[14] and involve the process known as lenition, in which the consonant is changed into a "weaker" form. This occurs in some (but not all) of the oblique case forms. For geminates, the process is simple to describe: they become simple stops, e.g. kuppi + -n → kupin (Finnish: "cup"). For simple consonants, the process complicates immensely and the results vary by the environment. For example, haka + -n → haan, kyky + -n → kyvyn, järki + -n → järjen (Finnish: "pasture", "ability", "intellect"). The specifics of consonants gradation vary by language (see the separate article for more details). Apocope (strongest in Livonian, Võro and Estonian) has, in some cases, left a phonemic status to the phonological variation in the stem (variation caused by the now historical morphological elements), which results in three phonemic lengths in these languages.
Vowel harmony is also characteristic of the Finnic languages, despite having been lost in Livonian, Estonian and Veps.
The original Uralic palatalization was lost in proto-Finnic,[15] but most of the diverging dialects reacquired it. Palatalization is a part of the Estonian literary language and is an essential feature in Võro, as well as Veps, Karelian, and other eastern Finnic languages. It is also found in East Finnish dialects, and is only missing from West Finnish dialects and Standard Finnish.[14]
A special characteristic of the languages is the large number of diphthongs. There are 16 diphthongs in Finnish and 25 in Estonian; at the same time the frequency of diphthong use is greater in Finnish than in Estonian due to certain historical long vowels having diphthongised in Finnish but not in Estonian.[14] On a global scale the Finnic languages have a high number of vowels.[16]
Subgrouping
[edit]The Finnic languages form a complex dialect continuum with few clear-cut boundaries.[17] Innovations have often spread through a variety of areas,[18] even after variety-specific changes.[citation needed]
A broad twofold conventional division of the Finnic varieties recognizes the Southern Finnic and Northern Finnic groups (though the position of some varieties within this division is uncertain):[19]
|
|
† = extinct variety; (†) = moribund variety.
A more-or-less genetic subdivision can be also determined, based on the relative chronology of sound changes within varieties, which provides a rather different view. The following grouping follows among others Sammallahti (1977),[20] Viitso (1998), and Kallio (2014):[21]
- Finnic
- South Estonian (Inland Finnic)
- Coastal Finnic
- Livonian (Gulf of Riga Finnic)
- Gulf of Finland Finnic
The division between South Estonian and the remaining Finnic varieties has isoglosses that must be very old. For the most part, these features have been known for long. Their position as very early in the relative chronology of Finnic, in part representing archaisms in South Estonian, has been shown by Kallio (2007, 2014).[15][21]
| Clusters *kt, *pt | Clusters *kc, *pc (IPA: *[kts], *[pts]) |
Cluster *čk (IPA: *[tʃk]) |
3rd person singular marker | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Estonian | *kt, *pt > tt | *kc, *pc > ts | *čk > tsk | endingless |
| Coastal Finnic | *kt, *pt > *ht | *kc, *pc > *ks, *ps | *čk > *tk | *-pi |
However, due to the strong areal nature of many later innovations, this tree structure has been distorted and sprachbunds have formed. In particular, South Estonian and Livonian show many similarities with the Central Finnic group that must be attributed to later contact, due to the influence of literary North Estonian.[19] Thus, contemporary "Southern Finnic" is a sprachbund that includes these languages, while diachronically they are not closely related.
The genetic classification of the Finnic dialects that can be extracted from Viitso (1998) is:
- Finnic
- Livonian (Gulf of Riga Finnic)
- South Estonian (Inland Finnic)
- Gulf of Finland Finnic
Viitso (2000)[22] surveys 59 isoglosses separating the family into 58 dialect areas (finer division is possible), finding that an unambiguous perimeter can be set up only for South Estonian, Livonian, Votic, and Veps. In particular, no isogloss exactly coincides with the geographical division into 'Estonian' south of the Gulf of Finland and 'Finnish' north of it. Despite this, standard Finnish and Estonian are not mutually intelligible.
Southern Finnic
[edit]The Southern Finnic languages consist of North and South Estonian (excluding the Coastal Estonian dialect group), Livonian and Votic (except the highly Ingrian-influenced Kukkuzi Votic). These languages are not closely related genetically, as noted above; it is a paraphyletic grouping, consisting of all Finnic languages except the Northern Finnic languages.[19] The languages nevertheless share a number of features, such as the presence of a ninth vowel phoneme õ, usually a close-mid back unrounded /ɤ/ (but a close central unrounded /ɨ/ in Livonian), as well as loss of *n before *s with compensatory lengthening.
(North) Estonian-Votic has been suggested to possibly constitute an actual genetic subgroup (called varyingly Maa by Viitso (1998, 2000) or Central Finnic by Kallio (2014)[21]), though the evidence is weak: almost all innovations shared by Estonian and Votic have also spread to South Estonian and/or Livonian. A possible defining innovation is the loss of *h after sonorants (*n, *l, *r).[21]
Northern Finnic
[edit]The Northern Finnic group has more evidence for being an actual historical/genetic subgroup. Phonetical innovations would include two changes in unstressed syllables: *ej > *ij[citation needed], and *o > ö after front-harmonic vowels. The lack of õ in these languages as an innovation rather than a retention has been proposed, and recently resurrected.[21] Germanic loanwords found throughout Northern Finnic but absent in Southern are also abundant, and even several Baltic examples of this are known.
Northern Finnic in turn divides into two main groups. The most Eastern Finnic group consists of the East Finnish dialects as well as Ingrian, Karelian and Veps; the proto-language of these was likely spoken in the vicinity of Lake Ladoga.[20] The Western Finnic group consists of the West Finnish dialects, originally spoken on the western coast of Finland, and within which the oldest division is that into Southwestern, Tavastian and Southern Ostrobothnian dialects. Among these, at least the Southwestern dialects have later come under Estonian influence.
Numerous new dialects have also arisen through contacts of the old dialects: these include e.g. the more northern Finnish dialects (a mixture of West and East Finnish), and the Livvi and Ludic varieties (probably originally Veps dialects but heavily influenced by Karelian).
Salminen (2003)[citation needed] present the following list of Finnic languages and their respective number of speakers.
| Language | Number of speakers | Geographical area |
|---|---|---|
| Livonian | 210 (second language) | Latvia |
| Võro-Seto | 50,000 | Estonia, Russia |
| Estonian | 1,000,000 | Mainly Estonia |
| Votic | 4 | Russia |
| Finnish | 5,000,000 | Mainly Finland |
| Ingrian | 200 | Russia |
| Karelian | 36,000 | Finland, Russia |
| Veps | 5,000 | Russia |
List of Finnic innovations
[edit]These features distinguish Finnic languages from other Uralic families:
Sound changes
[edit]Sound changes shared by the various Finnic languages include the following:[15][23]
- Development of long vowels and various diphthongs from loss of word-medial consonants such as *x, *j, *w, *ŋ.
- Before a consonant, the Uralic "laryngeal" *x posited on some reconstructions yielded long vowels at an early stage (e.g. *tuxli 'wind' > tuuli), but only the Finnic branch clearly preserves these as such. Later, the same process occurred also between vowels (e.g. *mëxi 'land' > maa).
- Semivowels *j, *w were usually lost when a root ended in *i and contained a preceding front (in the case of *j, e.g. *täji 'tick' > täi) or rounded vowel (in the case of *w, e.g. *suwi 'mouth' > suu).
- The velar nasal *ŋ was vocalized everywhere except before *k, leading to its elimination as a phoneme. Depending on the position, the results included semivowels (e.g. *joŋsi 'bow' > jousi, *suŋi 'summer'> suvi) and full vocalization (e.g. *jäŋi 'ice' > jää, *müŋä 'backside' > Estonian möö-, Finnish myö-).
- The development of an alternation between word-final *i and word-internal *e, from a Proto-Uralic second syllable vowel variously reconstructed as *i (as used in this article), *e or *ə.
- Elimination of all Proto-Uralic palatalization contrasts: *ć, *δ́, *ń, *ś > *c, *δ, *n, *s.
- Elimination of the affricate *č, merging with *š or *t, and the spirant *δ, merging with *t (e.g. *muδ́a 'earth' > muta). See above, however, on treatment of *čk.
- Assibilation of *t (from any source) to *c [t͡s] before *i. This later developed to /s/ widely: hence e.g. *weti 'water' > Estonian and Finnish vesi (cf. retained /t/ in the partitive *wet-tä > Estonian vett, Finnish vettä).
- Consonant gradation, most often for stops, but also found for some other consonants.
- A development *š > h, which, however, postdated the separation of South Estonian.
Superstrate influence of the neighboring Indo-European language groups (Baltic and Germanic) has been proposed as an explanation for a majority of these changes, though for most of the phonetical details the case is not particularly strong.[24]
Grammatical changes
[edit]- Agreement of the attributes with the noun, e.g. in Finnish vanho·i·lle mieh·i·lle "to old men" the plural -i- and the case -lle is added also to the adjective.
- Use of a copula verb like on, e.g. mies on vanha "the man is old".
- A tense system with present, preterite, perfect and pluperfect tenses.
- The shift of the proto-Uralic locative *-nA and the ablative *-tA into new, cross-linguistically uncommon functions: the former becoming the essive case, the latter the partitive case.
- This resulted in the rise of the telicity contrast of the object, which must be in the accusative case or partitive case.
- The rise of two new series of locative cases, the "inner locative" series marked by an element *-s-, and the "outer locative" marked by an element *-l-.
- The inessive *-ssA and the adessive *-llA were based on the original Uralic locative *-nA, with the *n assimilated to the preceding consonant.
- The elative *-stA and the ablative *-ltA similarly continue the original Uralic ablative *-tA.
- The origin of the illative *-sen and the allative *-len is less clear.
- The element *-s- in the first series has parallels across the other more western Uralic languages, sometimes resulting in formally identical case endings (e.g. an elative ending *-stē ← *-s-tA is found in the Sámi languages, and *-stə ← *s-tA in the Mordvinic languages), though its original function is unclear.
- The *-l- in the 2nd series likely originates by way of affixation and grammaticalization of the root *ülä- "above, upper" (cf. the prepositions *üllä ← *ül-nä "above", *ültä "from above").
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Other variants of the name include Balto-Finnic, Fennic, Balto-Fennic and Baltic Fennic languages. The term Finnic languages has also been used as a synonym of the extensive group of Finno-Permic languages, including the Baltic Finnic, Permic, Sámi, Mari and Mordvin languages.[3] This branch is now considered obsolete.
Citations
[edit]- ^ Rantanen, Timo; Tolvanen, Harri; Roose, Meeli; Ylikoski, Jussi; Vesakoski, Outi (8 June 2022). "Best practices for spatial language data harmonization, sharing and map creation—A case study of Uralic". PLOS ONE. 17 (6): e0269648. Bibcode:2022PLoSO..1769648R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0269648. PMC 9176854. PMID 35675367.
- ^ Rantanen, Timo, Vesakoski, Outi, Ylikoski, Jussi, & Tolvanen, Harri. (2021). Geographical database of the Uralic languages (v1.0) [Data set]. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4784188
- ^ Ruhlen, Merritt (1991). "Uralic-Yukaghir". A Guide to the World's Languages: Classification. Stanford University Press. p. 69. ISBN 0-8047-1894-6. Archived from the original on 19 April 2023. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- ^ Abondolo, Daniel Mario; Valijärvi, Riitta-Liisa, eds. (2023). The Uralic languages. Routledge language family (2nd ed.). London New York: Routledge. p. 91. ISBN 978-1-138-65084-8.
- ^ a b Junttila, Santeri (2010). "Itämerensuomen seuraava etymologinen sanakirja" (PDF). In Saarinen, Sirkka; Siitonen, Kirsti; Vaittinen, Tanja (eds.). Sanoista Kirjakieliin. Juhlakirja Kaisa Häkkiselle 17. Marraskuuta 2010. Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran Toimituksia. Vol. 259. ISSN 0355-0230. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- ^ Finnic Peoples Archived 7 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine at Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ Abondolo, Daniel, ed. (1998). The Uralic Languages. Routledge Language Family Descriptions. Taylor & Francis.
- ^ a b "Meänkieli, yksi Ruotsin vähemmistökielistä – Kielikello". www.kielikello.fi (in Finnish). Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Pajusalu, Karl (2009). "The reforming of the Southern Finnic language area" (PDF). Mémoires de la Société Finno-Ougrienne. 258: 95–107. ISSN 0355-0230. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ Söderholm, Eira. "Kainulaiset eli kväänit". Kainun Institutti – Kvensk Institutt (in Kven). Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ^ Jazyk. "Uralic migrations" (PDF). www.phil.muni.cz. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2019.
- ^ Kallio, Petri (2014). "The Diversification of Proto-Finnic". In Ahola, Joonas; Frog (eds.). Fibula, Fabula, Fact: The Viking Age in Finland (Studia Fennica Historica 18). Helsinki, Finland: Finno-Ugric Society. p. 163f. Archived from the original on 3 June 2022. Retrieved 27 December 2019.
- ^ Piispanen, Peter S. (2016). "Statistical Dating of Finno-Mordvinic Languages through Comparative Linguistics and Sound Laws" (PDF). Fenno-Ugrica Suecana Nova Series. 15: 12. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 May 2022. Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ^ a b c d Sinor, Denis (1988). The Uralic Languages: Description, History and Foreign Influences. BRILL. ISBN 90-04-07741-3. Archived from the original on 19 April 2023. Retrieved 13 December 2015 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b c Kallio, Petri (2007). "Kantasuomen konsonanttihistoriaa" (PDF). Mémoires de la Société Finno-Ougrienne (in Finnish). 253: 229–250. ISSN 0355-0230. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 July 2018. Retrieved 28 May 2009.
- ^ Feature 2A: Vowel Quality Inventories Archived 21 June 2019 at the Wayback Machine at World Atlas of Language Structures
- ^ Laakso 2001, p. 207.
- ^ Laakso 2001, p. 180.
- ^ a b c Viitso 1998, p. 101.
- ^ a b Sammallahti, Pekka (1977). "Suomalaisten esihistorian kysymyksiä" (PDF). Virittäjä: 119–136. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 November 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ^ a b c d e Kallio, Petri (2014). "The Diversification of Proto-Finnic". In Frog; Ahola, Joonas; Tolley, Clive (eds.). Fibula, Fabula, Fact. The Viking Age in Finland. Studia Fennica Historica. Vol. 18. Helsinki: Suomalaisen Kirjallisuuden Seura. ISBN 978-952-222-603-7.
- ^ Viitso, Tiit-Rein (2000). Finnic Affinity. Congressus Nonus Internationalis Fenno-Ugristarum I: Orationes plenariae & Orationes publicae. Tartu.
- ^ Posti, Lauri (1953). "From Pre-Finnic to Late Proto-Finnic". Finnische-Ugrische Forschungen. Vol. 31.
- ^ Kallio, Petri (2000). "Posti's superstrate theory at the threshold of a new millennium". In Laakso, Johanna (ed.). Facing Finnic: Some Challenges to Historical and Contact Linguistics. Castrenianumin toimitteita. Vol. 59.
References
[edit]- Laanest, Arvo (1975). Sissejuhatus läänemeresoome keeltesse (in Estonian). Tallinn: Eesti NSV Teaduste Akadeemia, Keele ja Kirjanduse Instituut.
- Laanest, Arvo (1982). Einführung in die ostseefinnischen Sprachen (in German). Translated by Laanest. Hamburg: Buske.
- Kettunen, Lauri (1960). "Suomen lähisukukielten luonteenomaiset piirteet". Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran Toimituksia. Vol. 119.
- Laakso, Johanna (2001). "The Finnic languages: Typology and contact". In Dahl, Ö.; Koptjevskaja-Tamm, M. (eds.). The Circum-Baltic languages. Vol. I: Past and Present. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
- Laakso, Johanna, ed. (2000). "Facing Finnic: Some challenges to historical and contact linguistics". Castrenianumin toimitteita. Vol. 59. Helsinki: Helsingin yliopisto.
- Setälä, E. N. (1891–1937). Yhteissuomalainen äännehistoria. Helsinki: Suomalaisen kirjallisuuden seura.
- Viitso, Tiit-Rein (1998). "Fennic". In Abondolo, Daniel (ed.). Uralic languages. Routledge.
External links
[edit]- Salminen, Tapani A. "Problems in the taxonomy of the Uralic languages in the light of modern comparative studies". Helsinki.
- Schalin, J. (ed.). "Lexicon of Early Indo-European loanwords preserved in Finnish".
- Swadesh list for Finnic languages (from Wiktionary's "Swadesh-list appendix". 22 January 2022.)