Arteriolosclerosis
| Arteriolosclerosis | |
|---|---|
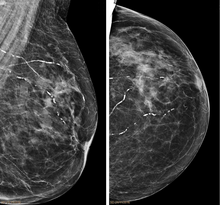 | |
| Right breast mammograms showing several calcified arterioles. Patient 94 years old. | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
Arteriolosclerosis is a form of cardiovascular disease involving hardening and loss of elasticity of arterioles or small arteries and is most often associated with hypertension and diabetes mellitus.[1] Types include hyaline arteriolosclerosis and hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis,[2] both involved with vessel wall thickening and luminal narrowing that may cause downstream ischemic injury. The following two terms whilst similar, are distinct in both spelling and meaning and may easily be confused with arteriolosclerosis.
- Arteriosclerosis is any hardening (and loss of elasticity) of medium or large arteries (from the Greek arteria, meaning artery, and sclerosis, meaning hardening)
- Atherosclerosis is a hardening of an artery specifically due to an atheromatous plaque. The term atherogenic is used for substances or processes that cause atherosclerosis.

Hyaline arteriolosclerosis
[edit]Also arterial hyalinosis and arteriolar hyalinosis refers to thickening of the walls of arterioles by the deposits that appear as homogeneous pink hyaline material in routine staining.[3] It is a type of arteriolosclerosis, which refers to thickening of the arteriolar wall and is part of the aging process.[4]
- Associations
It is associated with aging, hypertension, diabetes mellitus,[5] dementia,[6] and may be seen in response to certain drugs (calcineurin inhibitors).[7]
It is often seen in the context of kidney pathology.[4][8][9] In hypertension only the afferent arteriole is affected, while in diabetes mellitus, both the afferent and efferent arteriole are affected.[8][9] It is also seen in retina and brain,[10] where retinal infarcts and small brain infarcts, or lacunes can occur.
- Cause
Lesions reflect leakage of plasma components across vascular endothelium and excessive extracellular matrix production by smooth muscle cells, usually secondary to hypertension.[11]
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis is a major morphologic characteristic of benign nephrosclerosis, in which the arteriolar narrowing causes diffuse impairment of renal blood supply, with loss of nephrons.[5] The narrowing of the lumen can decrease renal blood flow and hence glomerular filtration rate leading to increased renin secretion and a perpetuating cycle with increasing blood pressure and decreasing kidney function.[12]
The brain is another organ where hyaline arteriolosclerosis occurs prematurely in patients with high blood pressure. This can cause either kind of stroke: an ischemic infarct or a brain hemorrhage, as the vessels can be blocked or broken.[13]
Hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis
[edit]
This is a type of arteriolosclerosis involving a narrowed lumen.[4] The term "onion-skin" is sometimes used to describe this form of blood vessel[14] with thickened concentric smooth muscle cell layer and thickened, duplicated basement membrane. In malignant hypertension these hyperplastic changes are often accompanied by fibrinoid necrosis of the arterial intima and media. These changes are most prominent in the kidney and can lead to ischemia and acute kidney failure. In the brain, a small cavity called a lacune is an ischemic cavity that can arise due to brain necrosis, due to arteriolosclerosis.[15][16]
- Cause
It can be caused by chronic benign (essential) hypertension[17] malignant hypertension.[4][18]
References
[edit]- ^ Robbins, Stanley L.; Kumar, Vinay (2007). Robbins basic pathology. Saunders/Elsevier. p. 343. ISBN 978-0-8089-2366-4.
- ^ "Arteriolosclerosis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Gamble CN (March 1986). "The pathogenesis of hyaline arteriolosclerosis". Am. J. Pathol. 122 (3): 410–20. PMC 1888226. PMID 2420184.
- ^ a b c d Thomas H. McConnell (2007). The Nature of Disease: Pathology for the Health Professions. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 277–. ISBN 978-0-7817-5317-3.
- ^ a b Robbins, Stanley L.; Kumar, Vinay (2007). Robbins basic pathology. Saunders/Elsevier. p. 356. ISBN 978-0-8089-2366-4.
- ^ Hainsworth AH, Markus HS, Schneider JA (2024). "Cerebral Small Vessel Disease, Hypertension, and Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia". Hypertension. 81 (1): 75–86. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.123.19943. PMC 10734789. PMID 38044814.
- ^ Yagisawa T, Omoto K, Shimizu T, Ishida H, Tanabe K (2015). "Arteriosclerosis in zero-time biopsy is a risk factor for tacrolimus-induced chronic nephrotoxicity". Nephrology (Carlton). 20 Suppl 2: 51–7. doi:10.1111/nep.12461. PMID 26031587.
- ^ a b Stout LC, Kumar S, Whorton EB (1994). "Insudative lesions--their pathogenesis and association with glomerular obsolescence in diabetes: a dynamic hypothesis based on single views of advancing human diabetic nephropathy". Human Pathology. 25 (11): 1213–1227. doi:10.1016/0046-8177(94)90039-6. PMID 7959667.
- ^ a b Najafian B, Alpers CE, Fogo AB (2011). "Pathology of human diabetic nephropathy". Contributions to Nephrology. 170: 36–47. doi:10.1159/000324942. PMID 21659756.
- ^ Lindley RI, Wang JJ, Wong MC, Mitchell P, Liew G, Hand P, Wardlaw J, De Silva DA, Baker M, Rochtchina E, Chen C, Hankey GJ, Chang HM, Fung VS, Gomes L, Wong TY (2009). "Retinal microvasculature in acute lacunar stroke: a cross-sectional study". Lancet Neurology. 8 (7): 628–634. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70131-0. PMID 19481977.
- ^ Eva Brehmer-Andersson (2006-08-02). Dermatopathology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 75–. ISBN 978-3-540-30244-5.
- ^ Sealey JE, von Lutterotti N, Rubattu S, Campbell WG Jr, Gahnem F, Halimi JM, Laragh JH (1991). "The greater renin system. Its prorenin-directed vasodilator limb. Relevance to diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, and hypertension". American Journal of Hypertension. 4 (12 Part 1): 972–977. doi:10.1093/ajh/4.12.972. PMID 1815656.
- ^ Sutherland GR, Auer RN (2006). "Primary intracerebral hemorrhage". Journal of Clinical Neuroscience. 13 (5): 511–517. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2004.12.012. PMID 16769513.
- ^ "Pathology Education". Archived from the original on 2006-09-01. Retrieved 2009-01-12.
- ^ Fisher CM (December 1968). "The arterial lesions underlying lacunes". Acta Neuropathologica. 12 (1): 1–15. doi:10.1007/BF00685305. PMID 5708546.
- ^ Fisher CM (1971). "Pathological observations in hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage". Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology. 30 (3): 536–550. doi:10.1097/00005072-197107000-00015. PMID 4105427.
- ^ Laurent, Stéphane; Boutouyrie, Pierre (2015). "The structural factor of hypertension: large and small artery alterations". Circulation Research. 116 (6): 1007-0021. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303596. PMID 25767286.
- ^ "Atherosclerosis". Retrieved 2009-01-12.
