Anti-Normanism
Normanism and anti-Normanism are competing groups of theories about the origin of Kievan Rus' that emerged in the 18th and 19th centuries concerning the narrative of the Viking Age in Eastern Europe. At the centre of the disagreement is the origin of the Varangian Rus', a people who travelled across and settled in Eastern Europe in the 8th and 9th centuries, and are considered by most modern historians to be of Scandinavian origin, eventually assimilated with the Slavs. The Normanist theory has been firmly established as mainstream, and modern Anti-Normanism is viewed as historical revisionism.
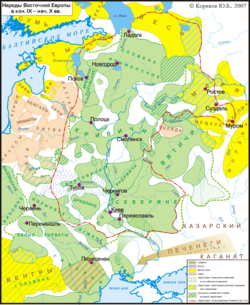
The origin of Kievan Rus' is infamously contentious, and relates to its perceived importance for the legitimation of nation-building, imperialism, and independence movements within the East Slavic-speaking world, and for legitimating different political relationships between eastern and western European countries. The Norsemen that ventured from what is now Sweden, into the waterways of Eastern Europe feature prominently in the history of the Baltic states, Scandinavia, Poland, and the Byzantine Empire.[1][2][3][4][5][6][7] They are particularly important in the historiography and cultural history of Belarus, Russia and Ukraine, but have also featured in the history of Poland.[8] Nevertheless, contention has centred around whether the development of Kievan Rus' was influenced by non-Slavic Varangians (this idea is characterised as the "Normanist theory"), or whether the people of Kievan Rus' emerged solely from autochthonous Slavic political development (known as the "anti-Normanist theory"),[9] including some other anti-Normanist and skeptical theories stemming from the scarcity of contemporary evidence for the emergence of Kievan Rus', and the great ethnic diversity and complexity of the wide area where these Norsemen were active.[10]
Mainstream view: Normanism
[edit]

Whereas the term "Normans" in English usually refers to the Scandinavian-descended ruling dynasty of Normandy in France from the 10th century onwards, and their scions elsewhere in Western Europe, in the context of the Rus' people, "Normanism" is the idea that the Rus' had their origins among the Normans (i.e. among "Northmen").[9] The term "Normanism" was used to cover a range of opinions about the degree of influence of the Varangians in the early history of Kievan Rus. The idea that Varangians founded Rus was seen politically unacceptable by many Russian historians.[11] Nevertheless, the close connection of Rus' with Scandinavians is confirmed by both archaeological evidence for extensive Scandinavian settlement in Russia and Ukraine,[12] and Slavic influences in the Swedish language.[13][14]
Early scholarship
[edit]Modern studies of the Rus' began when the German historian Gerhardt Friedrich Müller (1705–1783) was invited to work in the Russian Academy of Sciences in 1725.[15] Müller presented research made by his predecessor Gottlieb-Siegfried Bayer in the papers De Varagis ("On the Varangians", 1729) and Origines russicae ("Russian origins", 1736), and on the Primary Chronicle, written in the 12th century, and covering the years 852 to 1110. At the beginning of an important speech in 1749, later published as Origines gentis et nominis Russorum ("The Origins of the People and the Name of the Russians"), Müller argued that the Rurikid dynasty descended from ethnically Scandinavian Varangians and that the term "Russia" originated from Old Norse.[16][17] This statement caused such uproar in his Russian audience that he was unable to finish his presentation, and appeals to the president of the academy and the Empress led to the formation of a committee to determine if his research was "harmful to the interests and glory of the Russian Empire".[18] Before the committee, scathing criticism from Lomonosov, Krasheninnikov, and other Russian historians led to Müller being forced to suspend his work on the issue until Lomonosov's death. It was even thought during the 20th century that much of his research was destroyed, but recent research suggests that this is not the case: Müller managed to rework it and had it reprinted as Origines Rossicae in 1768.[11]: 58–59
Despite the negative reception in the mid-18th century, by the end of the century, Müller's views were the consensus in Russian historiography, and this remained largely the case through the 19th century and early 20th centuries.[16][19] Russian historians who accepted this historical account included Nikolai Karamzin (1766–1826) and his disciple Mikhail Pogodin (1800–1875), who gave credit to the claims of the Primary Chronicle that the Varangians were invited by East Slavs to rule over them and bring order.
The theory was not without political implications. For some, it fitted with embracing and celebrating the multiethnic character of the Russian Empire.[16] However, it was also consistent with the racial theory widespread at the time that Germanics (and their descendants) were naturally suited to government, whereas Slavs were not.[20][21][22] According to Karamzin, the Norse migration formed the basis and justification for Russian autocracy (as opposed to anarchy of the pre-Rurikid period), and Pogodin used the theory to advance his view that Russia was immune to social upheavals and revolutions, because the Russian state originated from a voluntary treaty between the people of Novgorod and Varangian rulers. The German-born Moscow academician August Ludwig von Schlözer said in 1802 that the Slavs had been living like "savage beasts and birds" before the advent of the civilizing Norsemen, a view later adopted by several scholars as well as non-scholars such as Adolf Hitler in the 20th-century, who saw in Russia "a wonderful instance of the state-organizing capability of the Germans among an inferior race".[23]
Emergence of Western scholarly consensus
[edit]During the historical debates of the 20th century, the key evidence for the mainstream view that Scandinavian migrants had an important role in the formation of Kievan Rus' emerged as the following:
- Notwithstanding other suggestions, the name Rus' can readily be interpreted as originating in Old Norse.[24][25]
- The personal names of the first few Rus' leaders are etymologically Old Norse, from Rurik (from Old Norse "Hrærekr") down to Olga of Kiev (from Old Norse "Helga"). Starting with Olga's son Sviatoslav I of Kiev onwards, Slavic names take over.[26]
- The list of cataracts on the Dnieper listed by Constantine VII in his De Administrando Imperio as belonging to the language of the Rhos can most readily be etymologised as Old Norse.[27][26]
- The Annals of St. Bertin account of the Rhos for 839 has them identify themselves as sueoni (Swedes).[28][29][30]
- 13th-century Icelandic historiography portrays close connections between the 11th-century rulers of Rus' and Scandinavian dynasties in England and Norway.[26]
In the 21st century, analyses of the rapidly growing range of archaeological evidence further noted that high-status 9th- to 10th-century burials of both men and women in the vicinity of the Upper Volga exhibit material culture largely consistent with that of Scandinavia (though this is less the case away from the river, or further downstream). This has been seen as further demonstrating the Scandinavian character of elites in Old Rus'.[31][32]
It is also agreed, however, that ancestrally Scandinavian Rus' aristocrats, like Scandinavians elsewhere, swiftly assimilated culturally to a Slavic identity: in the words of F. Donald Logan, "in 839, the Rus were Swedes; in 1043 the Rus were Slavs".[33] This relatively fast integration is noteworthy, and the processes of cultural assimilation in Rus' are an important area of research.[33][34]
The old Normanist assumption was that the Scandinavians introduced civilization to their Slavic subjects, but the number of Norsemen was relatively small compared to the number of Slavs and non-Slavs.[23] In addition, the Norsemen married local women, had their weapons made by Slavs, and only a relatively small number of Norse loanwords in Russian have been established.[23] In general, the Norsemen absorbed culture in Russia and down the Volga.[23]
There is uncertainty as to how large the Scandinavian migration to Rus' was, but some archaeological work in the years around 2000 argued for a substantial number of free farmers settling in the upper Volga region.[35][36]
Anti-Normanism
[edit]
Proponents of anti-Normanism are of the opinion that a state was founded by the Slavs even before the vocation of Rurik.[26][23] Starting with Mikhail Lomonosov (1711–1765), Slavophilic scholars have criticised the idea of Norse invaders.[37] By the early 20th century, the traditional anti-Normanist doctrine (as articulated by Dmitry Ilovaisky)[citation needed] seemed to have lost currency. Russian and then Soviet historians began to downplay the idea of Scandinavian influence in early Russian history.[23] The anti-Normanist arguments were revived and adopted in official Soviet historiography,[38][6][37] partly in response to Nazi propaganda, which posited that Russia owed its existence to a Germanic ruling elite.[39] In the earlier 20th century, Nazi Germany had promoted the idea that Russia owed its statehood to a Germanic, racially superior, elite.[39] Mikhail Artamonov ranks among those who attempted to reconcile both theories by hypothesizing that the Kievan state united the southern Rus' (of Slavic stock) and the northern Rus' (of Germanic stock) into a single nation.[40]
In light of evidence, theories – most of them proposed by Soviet scholars with nationalistic agendas – of a Slav state in the Baltic region attacked by and ultimately absorbing Viking invaders are more likely the product of wishful thinking than of fact.
Waldman, & Mason 2005, p. 668
The staunchest advocate of the anti-Normanist views in the period following the Second World War was Boris Rybakov, who argued that the cultural level of the Varangians could not have warranted an invitation from the culturally advanced Slavs. This conclusion leads Slavicists to deny the Primary Chronicle, which writes that the Varangian Rus' were invited by the native Slavs. Rybakov assumed that Nestor, putative author of the Chronicle, was biased against the pro-Greek party of Vladimir Monomakh and supported the pro-Scandinavian party of the ruling prince Svyatopolk. He cites Nestor as a pro-Scandinavian manipulator and compares his account of Rurik's invitation with numerous similar stories found in folklore around the world.[citation needed]
By the 21st century, most professional scholars, in both Anglophone and Slavic-language scholarship, had reached a consensus that the origins of the Rus' people lay in Scandinavia and that this originally Scandinavian elite had a significant role in forming the polity of Kievan Rus'.[26][41][42][43] Indeed, in 1995, the Russian archaeologist Leo Klejn "gave a paper entitled 'The End of the Discussion', in the belief that anti-Normanism 'was dead and buried'". However, Klejn soon had to revise this opinion as anti-Normanist ideas gained a new prominence in both public and academic discourse in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus.[44] Anglophone scholarship has identified the continued commitment to anti-Normanism in these countries since the collapse of the Soviet Union as being motivated by present-day ethno-nationalism and state-formation.[45][11]: 63 One prominent Russian example occurred with an anti-Normanist conference in 2002, which was followed by publications on the same theme, and which appears to have been promoted by Russian government policy of the time.[46] Accordingly, anti-Normanist accounts are prominent in some 21st century Russian school textbooks.[47] Meanwhile, in Ukraine and to a lesser extent Belarus, post-Soviet nation-building opposed to a history of Russian imperialism has promoted anti-Normanist views in academia and, to a greater extent, popular culture.[48]
Other anti-Normanist interpretations
[edit]
There have been quite a few alternative, non-Normanist origins for the word Rus', although none was endorsed in the Western academic mainstream:
- Three early emperors of the Urartian Empire at Caucasus from 8th to 6th century BC had their names Russa I, Russa II and Russa III, documented in cuneiform monuments.
- The medieval legend of three brothers, one named Rus, had also its predecessor in very similar legend from ancient Armenians with almost the same classical name (studies by D. J. Marr). Furthermore, Kiev was founded centuries before the Rus' rule.
- The ancient Sarmatian tribe of the Roxolani (from the Ossetic, ruhs "light"; R русые волосы / rusyje volosy / "light-brown hair"; cf. Dahl's dictionary definition of Русь /rus/: Русь ж. в знач. мир, белсвет. Rus, fig. world, universe [белсвет: lit. "white world", "white light"]).
- From the Old Slavic name that meant "river-people" (tribes of fishermen and ploughmen who settled near the rivers Dnieper, Don, Dniester and Western Dvina and were known to navigate them). The rus root is preserved in the modern Slavic and Russian words ruslo (river-bed), rusalka (water sprite), etc.
- From one of two rivers in Ukraine (near Kiev and Pereyaslav), Ros and Rusna, whose names are derived from a postulated Slavic term for water, akin to rosa (dew) (related to the above theory).
- A Slavic word rusy (refers only to hair color – from dark ash-blond to light-brown), cognate with ryzhy ("red-haired") and English "red".
- A postulated proto-Slavic word for bear, cognate with Greek arctos and Latin ursus.
Other views
[edit]The controversies over the nature of the Rus and the origins of the Russian state have bedevilled Viking studies, and indeed Russian history, for well over a century. It is historically certain that the Rus were Swedes. The evidence is incontrovertible, and that a debate still lingers at some levels of historical writing is clear evidence of the holding power of received notions. The debate over this issue – futile, embittered, tendentious, doctrinaire – served to obscure the most serious and genuine historical problem which remains: the assimilation of these Viking Rus into the Slavic people among whom they lived. The principal historical question is not whether the Rus were Scandinavians or Slavs, but, rather, how quickly these Scandinavian Rus became absorbed into Slavic life and culture.
There are some Anglophone scholars who remain skeptical about the origin of Rus', however, either because the evidence is not good enough, or because they remain uncertain whether Rus' was an ethnic group with a clear point of origin.[1][50][51][52]
Scholars such as Omeljan Pritsak and Horace G. Lunt offer explanations that go beyond simplistic attempts to attribute "ethnicity" on first glance interpretation of literary, philological, and archaeological evidence. They view the Rus' as disparate, and often mutually antagonistic, clans of charismatic warriors and traders who formed wide-ranging networks across the North and Baltic Seas.[53][54] They were a "multi-ethnic, multilingual and non-territorial community of sea nomads and trading settlements" that contained numerous Norsemen—but equally Slavs, Balts, and Finns.[53]
Tolochko argues "the story of the royal clan's journey is a device with its own function within the narrative of the chronicle. ... Yet if we take it for what it actually is, if we accept that it is not a documentary ethnographic description of the 10th century, but a medieval origo gentis[a] masterfully constructed by a Christian cleric of the early 12th century, then we have to reconsider the established scholarly narrative of the earliest phase of East European history, which owes so much to the Primary Chronicle".[55]
Archaeological research, synthesizing a wide range of 20th-century excavations, has begun to develop what Jonathan Shepard has called a "bottom up" vision of the formation of the Rus' polity, in which, during the ninth and 10th century increasingly intensive trade networks criss-crossed linguistically and ethnically diverse groups around rivers like the Volga, the Don, the Dnieper. This may have produced "an essentially voluntary convergence of groupings in common pursuit of primary produce exchangeable for artefacts from afar".[56] This fits well with the image of Rus' that dominates the Arabic sources, focusing further south and east, around the Black and Caspian Seas, the Caucasus and the Volga Bulgars.[57] Yet this narrative, though plausible, contends with the "top-down" image of state development implied by the Primary Chronicle, archaeological assemblages indicating Scandinavian-style weapon-bearing elites on the Upper Volga, and evidence for slave-trading and violent destruction of fortified settlements.[58][59]
Numerous artefacts of Scandinavian affinity have been found in northern Russia (as well as artefacts of Slavic origin in Sweden). However, exchange between the north and southern shores of the Baltic had occurred since the Iron Age (albeit limited to immediately coastal areas).[60] Northern Russia and adjacent Finnic lands had become a profitable meeting ground for peoples of diverse origins, especially for the trade of furs, and attracted by the presence of oriental silver from the mid-8th century AD.[61] There is an undeniable presence of goods and people of Scandinavian origin; however, the predominant people remained the local (Baltic and Finnic) peoples.[62]
The increasing volume of trade and internal competition necessitated higher forms of organization. The Rus' appeared to emulate aspects of Khazar political organization—hence the mention of a Rus' chaganus in the Carolingian court in 839 (Royal Frankish Annals). Legitimization was sought by way of adopting a Christian and linguistically Slavic "high culture" that became the "Kievan Rus'".[63] Moreover, there is doubt if the emerging Kievan Rus' were the same clan as the "Rus" who visited the Carolingians in 839 or who attacked Constantinople in 860 AD.[64]
The rise of Kiev itself is mysterious. Devoid of any silver dirham finds in the 8th century AD, it was situated west of the profitable fur and silver trade networks that spanned from the Baltic to the Muslim lands, via the Volga–Kama basins. At the prime hill in Kiev, fortifications and other symbols of consolidation and power appear from the 9th century, thus preceding the literary appearance of "Rus" in the middle Dnieper region. By the 10th century, the lowlands around Kiev had extensive "Slavic" styled settlements, and there is evidence of growing trade with the Byzantine lands. This might have attracted Rus' movements, and a shift in power, from the north to Kiev.[65] Thus, Kiev does not appear to have evolved from the infrastructure of the Scandinavian trade networks, but rather it forcibly took them over, as evidenced by the destruction of numerous earlier trade settlements in the north, including the famous Staraya Ladoga.[66]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b P. B. Golden, "Rūs", in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition, Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C. E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel, W. P. Heinrichs. Retrieved on 26 July 2018. doi:10.1163/1573-3912_islam_COM_0942.
- ^ Roman Zakharii,"The Historiography of Normanist and Anti-Normanist theories on the origin of Rus': A review of modern historiography and major sources on Varangian controversy and other Scandinavian concepts of the origins of Rus' Archived 29 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine" (unpublished M.Phil. thesis, University of Oslo, 2002).
- ^ Wladyslaw Duczko, Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe (Leiden: Brill, 2004), pp. 3-9.
- ^ Serhii Plokhy, The Origins of the Slavic Nations Premodern Identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), pp. 10-48.
- ^ Christian Raffensperger, "The Place of Rus' in Medieval Europe[permanent dead link]", History Compass, 12/11 (2014), 853–65 doi:10.1111/hic3.12201 (pp. 853-54).
- ^ a b Elena Melnikova, "The 'Varangian Problem': Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics", in Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions, ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42-52.
- ^ History Time (1 August 2017), Vikings Of The East: Igor & The Kievan Rus', archived from the original on 14 March 2023, retrieved 20 February 2019
- ^ Stephen Velychenko (1992). National History as Cultural Process: A Survey of the Interpretations of Ukraine's Past in Polish, Russian, and Ukrainian Historical Writing from the Earliest Times to 1914. Canadian Institute of Ukrainian Studies Press. pp. 47–49. ISBN 978-0-920862-75-9. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- ^ a b Paul Robert Magocsi (18 June 2010). A History of Ukraine: The Land and Its Peoples (Second ed.). University of Toronto Press. pp. 56–58. ISBN 978-1-4426-9879-6. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- ^ Janet Martin, "The First East Slavic State", in A Companion to Russian History, ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 34-50 (pp. 34-36).
- ^ a b c Dmitry Nikolayevich Verkhoturov, "Normanism: What's in a Name?", Valla, 1.5 (2015), 57-65, citing Клейн Л.С. Норманизм – антинорманизм: конец дискуссии. // Stratum plus. 1999. №5, Неславянское в славянском мире. С. 91-101.
- ^ Hedenstierna-Jonson, C.; Losquiño, I.G. (2023). Viking Camps: Case Studies and Comparisons. Routledge Archaeologies of the Viking World. Taylor & Francis. p. 1991. ISBN 978-1-000-90576-2. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- ^ Williams, Tom (28 February 2014). "Vikings in Russia". blog.britishmuseum.org. The British Museum. Archived from the original on 21 January 2021. Retrieved 15 January 2021.
- ^ Simon Franklin and Jonathan Shepherd, The Emergence of Rus 750–1200 (Harlow, Essex: 1996), pp. 38–39.
- ^ Serhii Plokhy, Lost Kingdom: The Quest for Empire and the Making of the Russian Nation from 1740 to the Present (London: Allen Lane, 2017).
- ^ a b c Serhii Plokhy, Ukraine and Russia: Representations of the Past (Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2008), chapter 1.
- ^ Elena Melnikova, "The 'Varangian Problem': Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics', in Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions, ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42-52 (p. 43).
- ^ Pritsak, Omeljan, "The Origin of the Rus'", Russian Review, vol. 36, No. 3 (July 1977), pp. 249–273
- ^ Elena Melnikova, "The 'Varangian Problem': Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics", in Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions, ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42–52 (pp. 44–45).
- ^ Christian Promitzer, "Physical anthropology and ethnogenesis in Bulgaria, 1878–1944", Focaal—Journal of Global and Historical Anthropology, 58 (2010), 47–62 doi:10.3167/fcl.2010.580104 (pp. 49–50).
- ^ Cf. Richard Mcmahon, "Anthropological Race Psychology 1820–1945: A Common European System of Ethnic Identity Narratives", Nations and Nationalism, 15 (2009), 575–596 (p. 579).
- ^ Cf. Matthew H. Hammond, "Ethnicity and the Writing of Medieval Scottish History" Archived 25 March 2023 at the Wayback Machine, The Scottish Historical Review, vol. 85 (no. 219) (April 2006), 1–27, doi:10.1353/shr.2006.0014.
- ^ a b c d e f Pulsiano, Phillip (1993). Medieval Scandinavia: An Encyclopedia. Taylor & Francis. pp. 556–558. ISBN 978-0-8240-4787-0. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 14 March 2023.
- ^ Stefan Brink, "Who were the Vikings?", in The Viking World Archived 14 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine, ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4-10 (pp. 6-7).
- ^ "Russ, adj. and n." OED Online, Oxford University Press, June 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/169069. Accessed 12 January 2021.
- ^ a b c d e Omeljan Pritsak, "Rus'", in Medieval Scandinavia: An Encyclopedia Archived 26 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine, ed. by Phillip Pulsiano (New York: Garland, 1993), pp. 555-56.
- ^ H. R. Ellis Davidson, The Viking Road to Byzantium (London: Allen & Unwin, 1976), p. 83.
- ^ Duczko 2004, p. 10
- ^ Jonathan Shepard, "The Viking Rus and Byzantium", in The Viking World Archived 14 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine, ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 496-516 (p. 497).
- ^ Janet Martin (6 April 2009). "The First East Slavic State". In Abbott Gleason (ed.). A Companion to Russian History. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4443-0842-6.
- ^ Wladyslaw Duczko, Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe (Leiden: Brill, 2004).
- ^ Jonathan Shepherd, "Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics", English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104.
- ^ a b Logan 2005, p. 184 "The controversies over the nature of the Rus and the origins of the Russian state have bedevilled Viking studies, and indeed Russian history, for well over a century. It is historically certain that the Rus were Swedes. The evidence is incontrovertible, and that a debate still lingers at some levels of historical writing is clear evidence of the holding power of received notions. The debate over this issue - futile, embittered, tendentious, doctrinaire – served to obscure the most serious and genuine historical problem which remains: the assimilation of these Viking Rus into the Slavic people among whom they lived. The principal historical question is not whether the Rus were Scandinavians or Slavs, but, rather, how quickly these Scandinavian Rus became absorbed into Slavic life and culture."
- ^ Sherman, Heidi M. "The Normanist Controversy". encyclopedia.com. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ I. Jansson, "Warfare, Trade or Colonisation? Some General Remarks on the Eastern Expansion of the Scandinavians in the Viking Period", in The Rural Viking in Russia and Sweden, ed. by P. Hansson (Örebro, 1997), pp. 47–51.
- ^ Jonathan Shepherd, "Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics", English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 (pp. 395–96) doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104.
- ^ a b Ohlobyn, Oleksander. "Normanist theory". Internet Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Archived from the original on 7 September 2018. Retrieved 18 October 2021.
- ^ Janet Martin, "The First East Slavic State", in A Companion to Russian History, ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 34–50 (pp. 37–42).
- ^ a b Jonathan Shepherd, "Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics", English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104 (pp. 386–87).
- ^ Jonathan Shepherd, "Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics", English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104 (p. 387).
- ^ Wladyslaw Duczko, Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe (Leiden: Brill, 2004), esp. pp. 3–9.
- ^ Abbott Gleason, "Russian Historiography after the Fall", in A Companion to Russian History, ed. by Abbott Gleason (Oxford: Blackwell, 2009), pp. 1–14 (p. 5).
- ^ Elena Melnikova, "The 'Varangian Problem': Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics", in Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions, ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42–52 (p. 42).
- ^ Jonathan Shepherd, "Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics", English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104 (p. 387), citing Leo S. Klejn, Soviet Archaeology: Trends, Schools, and History, trans. by Rosh Ireland and Kevin Windle (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2012), p. 119.
- ^ Christian Raffensperger, "The Place of Rus' in Medieval Europe" Archived 10 August 2023 at the Wayback Machine, History Compass, 12/11 (2014), 853–865 doi:10.1111/hic3.12201 (esp. pp. 853–854, 858).
- ^ Elena Melnikova, "The 'Varangian Problem': Science in the Grip of Ideology and Politics", in Russia's Identity in International Relations: Images, Perceptions, Misperceptions, ed. by Ray Taras (Abingdon: Routledge, 2013), pp. 42–52, citing I. A. Nastenko (ed.), Sbornik Russkogo istoricheskogo obshchestva: "Antinormanism", vol 8. (no. 156) (Moscow: Russkaja Panorama, 2003) and V. V. Fomin, Varjagi i varjazhskaja Rus': Kitogam diskussii po varjazhskomu voprosu (Moscow: Russkaja Panorama, 2005).
- ^ Artem Istranin and Alexander Drono, "Competing historical Narratives in Russian Textbooks" Archived 10 August 2023 at the Wayback Machine, in Mutual Images: Textbook Representations of Historical Neighbours in the East of Europe, ed. by János M. Bak and Robert Maier, Eckert. Dossiers, 10 ([Braunschweig]: Georg Eckert Institute for International Textbook Research, 2017), 31–43 (pp. 35–36).
- ^ Serhii Plokhy, The Origins of the Slavic Nations Premodern Identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), pp. 10–48 (esp. pp. 11–12).
- ^ Logan 2005, p. 184
- ^ James E. Montgomery, "Ibn Faḍlān and the Rūsiyyah" Archived 16 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Journal of Arabic and Islamic Studies, 3 (2000), 1–25.
- ^ Andrii Danylenko, "The Name 'Rus' in Search of a New Dimension", Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas, new series, 52 (2004), 1–32.
- ^ Marika Mägi, "In Austrvegr: The Role of the Eastern Baltic in Viking Age Communication Across the Baltic Sea", The Northern World, 84 (Leiden: Brill, 2018), pp. 141–216.
- ^ a b Pritsak (1981, p. 14)
- ^ Lunt (1975, p. 271)
- ^ Tolochko (2008, p. 184 & 188, resp)
- ^ Jonathan Shepherd, "Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics", English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104 (pp. 389–402, quoting p. 397).
- ^ Thorir Jonsson Hraundal, "New Perspectives on Eastern Vikings/Rus in Arabic Sources", Viking and Medieval Scandinavia, 10 (2014), 65–69 doi:10.1484/J.VMS.5.105213 (pp. 70–71).
- ^ Jonathan Shepherd, "Review Article: Back in Old Rus and the USSR: Archaeology, History and Politics", English Historical Review, vol. 131 (no. 549) (2016), 384–405 doi:10.1093/ehr/cew104 (pp. 389–402).
- ^ Thorir Jonsson Hraundal, "New Perspectives on Eastern Vikings/Rus in Arabic Sources", Viking and Medieval Scandinavia, 10 (2014), 65–69 doi:10.1484/J.VMS.5.105213 (p. 71).
- ^ Franklin (1996, p. 9)
- ^ Franklin (1996, p. 12)
- ^ Franklin (1996, pp. 22–25)
- ^ Pritsak, p. 31
- ^ Tolochko, p. 187
- ^ Franklin (1996, pp. 90–122)
- ^ Tolochko p. 186
Bibliography
[edit]- The Annals of Saint-Bertin, transl. Janet L. Nelson, Ninth-Century Histories 1 (Manchester and New York, 1991).
- Davies, Norman. Europe: A History. New York: Oxford University Press, 1996.
- Bury, John Bagnell; Gwatkin, Henry Melvill (1936). The Cambridge Medieval History, Volume 3. University Press. ISBN 0415327563. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- Christian, David. A History of Russia, Mongolia, and Central Asia. Blackwell, 1999.
- Danylenko, Andrii. "The name Rus': In search of a new dimension." Jahrbueher fuer Geschichte Osteuropas 52 (2004), 1–32.
- Davidson, H.R. Ellis, The Viking Road to Byzantium. Allen & Unwin, 1976.
- Dolukhanov, Pavel M. The Early Slavs: Eastern Europe from the Initial Settlement to the Kievan Rus. New York: Longman, 1996.
- Duczko, Wladyslaw. Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe Archived 10 August 2023 at the Wayback Machine (The Northern World; 12). Leiden: Brill Academic Publishers, 2004 (hardcover, ISBN 90-04-13874-9).
- Goehrke, C. Frühzeit des Ostslaven. Darmstadt: Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft, 1992.
- Magocsi, Paul R. A History of Ukraine. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1996.
- Pritsak, Omeljan. The Origin of Rus'. Cambridge Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1991.
- Stang, Hakon. The Naming of Russia. Oslo: Middelelser, 1996.
- Gerard Miller as the author of the Normanist theory (Brockhaus and Efron)
- Logan, F. Donald (2005). The Vikings in History. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 0415327563. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- Lunt, Horace G. (1975). "On the Language of Old Rus: Some Questions and Suggestions". Russian Linguistics. 2 (3/4): 269–281. doi:10.1007/BF00221437. ISSN 0304-3487. JSTOR 40159848. S2CID 153939821.
- Franklin, Simon (1996). The emergence of Rus, 750-1200. London: Longman. ISBN 9780582490918.
- Pritsak, Omeljan (1981). The origin of Rus'. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674644656.
- Tolochko, Olksiy P. (2008). "The Primary Chronicle's 'Ethnography' Revisited: Slavs and Varangians in the Middle Dnieper Region and the Origin of the Rus' State". In Garipzanov, Ildar H.; Geary, Patrick J.; Urbańczyk, Przemysław (eds.). Franks, Northmen, and Slavs: Identities and State Formation in Early Medieval Europe. Brepols. pp. 169–188. ISBN 978-2-503-52615-7. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- Brink, Stefan; Price, Price (2008). The Viking World. Routledge. ISBN 978-1134318261. Archived from the original on 14 April 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- Duczko, Wladyslaw [in Polish] (2004). Viking Rus: Studies on the Presence of Scandinavians in Eastern Europe. Brill. ISBN 9004138749. Archived from the original on 14 April 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- Waldman, Carl; Mason, Catherine (2005). Encyclopedia of European Peoples. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 1438129181. Archived from the original on 11 March 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
External links
[edit]- James E. Montgomery, "Ibn Faḍlān and the Rūsiyyah", Journal of Arabic and Islamic Studies, 3 (2000), 1-25. Archive.org. Includes a translation of Ibn Fadlān's discussion of the Rūs/Rūsiyyah.
