Angström (crater)
 Apollo 15 image | |
| Coordinates | 29°54′N 41°36′W / 29.9°N 41.6°W[1] |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 9.55[1] km |
| Depth | 2.0 km |
| Colongitude | 42° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Anders J. Ångström[1] |


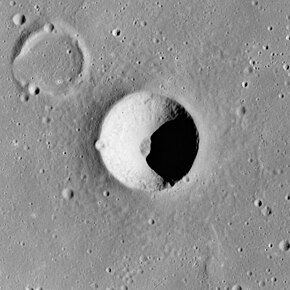
Ångström is a small lunar impact crater located on the border between Oceanus Procellarum to the west and Mare Imbrium to the east. To the south is a formation of mountains rising out of the mare named the Montes Harbinger. To the east are some wrinkle ridges named the Dorsum Bucher and Dorsa Argand. This crater is bowl-shaped, with a circular rim and inner walls that slope down to the small central floor. It has a higher albedo than the surrounding maria.[2] The crater halo is radar dark, indicating a lack of larger blocks among the fine ejecta.[3]
Ångström crater is named after Anders Jonas Ångström,[1] a Swedish physicist and one of the founders of the science of spectroscopy.
Satellite craters
[edit]By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Ångström.[2]
| Ångström | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 30.9° N | 41.1° W | 6 km |
| B | 31.7° N | 44.1° W | 6 km |
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ a b Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- ^ Ghent, Rebecca R.; et al. (February 2005). "Earth-based observations of radar-dark crater haloes on the Moon: Implications for regolith properties". Journal of Geophysical Research. 110 (E2): E02005. Bibcode:2005JGRE..110.2005G. doi:10.1029/2004JE002366. E02005.
Sources
[edit]- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763. S2CID 122125855.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
External links
[edit] Media related to Angstrom (crater) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Angstrom (crater) at Wikimedia Commons- LTO-39A2 Angstrom — detailed USGS topographic map of crater and vicinity

