N-Acetylgalactosamine
Appearance
(Redirected from Acetylgalactosamine)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
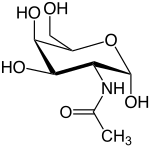
2-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-D-galactose
| |
| Other names
GalNAc; 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactose; N-Acetylchondrosamine; 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactopyranose; N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 221.21 g/mol |
| Melting point | 172 to 173 °C (342 to 343 °F; 445 to 446 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related monosaccharides
|
N-Acetylglucosamine Galactosamine Galactose |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), is an amino sugar derivative of galactose.
Function
[edit]In humans it is the terminal carbohydrate forming the antigen of blood group A.[1]
It is typically the first monosaccharide that connects serine or threonine in particular forms of protein O-glycosylation.
N-Acetylgalactosamine is necessary for intercellular communication, and is concentrated in sensory nerve structures of both humans and animals.
GalNAc is also used as a targeting ligand in investigational antisense oligonucleotides and siRNA therapies targeted to the liver, where it binds to the asialoglycoprotein receptors on hepatocytes. [2]
See also
[edit]- Galactosamine
- Globoside
- (N-Acetylglucosamine) GlcNAc
References
[edit]- ^ Donald M. Marcus; Elvin A. Kabat; Gerald Schiffman (1964). "Immunochemical Studies on Blood Groups. XXXI. Destruction of Blood Group A Activity by an Enzyme from Clostridium tertium Which Deacetylates N-Acetylgalactosamine in Intact Blood Group Substances". Biochemistry. 3 (3): 437–443. doi:10.1021/bi00891a023.
- ^ Nair, Jayaprakash K; Willoughby, Jennifer L. S; Chan, Amy; Charisse, Klaus; Alam, Md. Rowshon; Wang, Qianfan; Hoekstra, Menno; Kandasamy, Pachamuthu; Kel'In, Alexander V; Milstein, Stuart; Taneja, Nate; o'Shea, Jonathan; Shaikh, Sarfraz; Zhang, Ligang; Van Der Sluis, Ronald J; Jung, Michael E; Akinc, Akin; Hutabarat, Renta; Kuchimanchi, Satya; Fitzgerald, Kevin; Zimmermann, Tracy; Van Berkel, Theo J. C; Maier, Martin A; Rajeev, Kallanthottathil G; Manoharan, Muthiah (2014). "Multivalent N-Acetylgalactosamine-Conjugated siRNA Localizes in Hepatocytes and Elicits Robust RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 136 (49): 16958–16961. doi:10.1021/ja505986a. PMID 25434769.
External links
[edit] Media related to N-Acetylgalactosamine at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to N-Acetylgalactosamine at Wikimedia Commons
