Abat-son
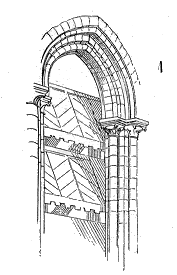
An abat-son (plural usually abat-sons) is an architectural device constructed to reflect or direct sound in a particular direction. It consists of large louvers. The term is commonly used to refer to angled louvers in a bell tower or belfry designed to redirect sound or to prevent ingress of water.[1]
Abat-son can also refer to a louver or board used in the device.[2][3] These boards or sheets are typically made of wood or metal.[4]
The term comes from the French abat-sons, literally abat 'it strikes down' and sons 'sounds'.[5][6]
In the windshields
[edit]The slats, generally of the grid type and fixed to a carpentry frame, are usually made of wood or covered with metal, slate or lead; In addition to redirecting the sound of the bells towards the ground, they prevent rain or snow from penetrating the bell tower and allow the tower's carpentry to be ventilated. «Beffroi», is an architectural technical Gallicism that appeared in the 19th century, replacing the popular name of «windscreen» (abat-vent).[7]
Loudspeakers are often inserted into twin bays on each of the steeple faces, more rarely in the skylights of steeple arrows. These vain bell towers are typically flanked by columns with capitals and decorations, in Romanesque architecture, with archivolts, and with interlocking fretwork in Gothic architecture. Turntables developed especially from the 13th century, and were often already decorated with fretwork, serrated bottoms, or embossed in lead.[8][failed verification]
Gallery
[edit]-
A church in Trélissac
-
Church of Saints Peter and Paul, La Tour-Blanche
-
Church of Our Lady of the Assumption, Échourgnac
References
[edit]- ^ Curl, James Stevens; Wilson, Susan (2015). The Oxford dictionary of architecture (Third ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-175298-8. OCLC 913074935.
- ^ Bond, Francis (1913). An Introduction to English Church Architecture from the Eleventh to the Sixteenth Century. London: H. Milford.
- ^ Montague, Don (2 September 2003). Dictionary of Building and Civil Engineering. doi:10.4324/9780203475430. ISBN 9781135821685.
- ^ Newmark, Maxim (15 January 1950). Dictionary of Foreign Words and Phrases. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-4422-3401-7.
- ^ "Definition of ABAT-SONS". www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- ^ Passy, Paul; Hempl, George (1904). International French-English and English-French Dictionary. Hinds, Noble & Eldredge.
- ^ Pierrel, Jean-Marie (25 November 2013). "Structuration et usage de ressources lexicales institutionnelles sur le français" (PDF). Ressources Lexicales. Lingvisticæ Investigationes Supplementa. Vol. 30. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. pp. 119–152. doi:10.1075/lis.30.04pie. ISBN 978-90-272-3140-6. HAL hal-00914295. Retrieved 26 March 2022.
- ^ Hillson, James (June 2017). Berenbeim, Jessica; Heslop, Sandy (eds.). "Imagining Invention: The Character of the 'Gothic architect' and England, 1200–1400". British Art Studies (6). doi:10.17658/issn.2058-5462/issue-06/jillson. Retrieved 26 March 2022.
Further reading
[edit]- Sturgis' Illustrated Dictionary of Architecture and Building: an unabridged reprint of the 1901-2 edition. Dover Pictorial Archive Series. Vol. I: A–E. New York: Dover Publications. 1989. p. 1. ISBN 0-486-26025-9. LCCN 89-1350.
External links
[edit] Media related to Abat-sons at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Abat-sons at Wikimedia Commons



