2-Quinolone
Appearance
(Redirected from 2-quinolone)

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Quinolin-2(1H)-one | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.382 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H7NO | |
| Molar mass | 145.161 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | solid |
| Melting point | 199.5 °C (391.1 °F; 472.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
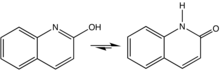
2-Quinolone is an organic compound related structurally to quinoline. It is the majority tautomer in equilibrium with 2-quinolinol. The compound can be classified as a cyclic amide, and as such is used as an isostere for peptides and other pharmaceutically inspired targets.[1][2] The 4-methyl-2-quinolone can be prepared by dehydration of acetoacetanilide.[3]
The isomer 4-quinolone is the parent of a large class of antibiotics called quinolone antibiotics. A prominent example is ciprofloxacin, a broad spectrum antibiotic commonly used for treatment of various infections such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), typhoid, meningitis, gonorrhoea, syphilis,[4] and skin infections.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ Tashima, Toshihiko (2015). "The structural use of carbostyril in physiologically active substances". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 25 (17): 3415–3419. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.06.027. PMID 26112444.
- ^ "2(1H)-Quinolinone". NIST. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ Lauer, W. M.; Kaslow, C. E. (1944). "4-Methylcarbostyril". Organic Syntheses. 24: 68. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.024.0068.
- ^ "Ciprofloxacin For The Treatment Of STDs: What You Need To Know | Allo Health". www.allohealth.care. 20 June 2023. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ^ "About ciprofloxacin". nhs.uk. 14 December 2022. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
External links
[edit] Media related to 2-Quinolone at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 2-Quinolone at Wikimedia Commons
