Punicafolin
Appearance
(Redirected from 1,2,4-tri-O-galloyl-3,6-(R)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-β-D-glucose)
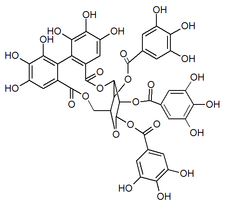
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
1,2,4-tri-O-galloyl-3,6-(R)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-β-D-glucose
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C41H30O26 | |
| Molar mass | 938.63 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Punicafolin is an ellagitannin from the leaves of Punica granatum (pomegranate)[1] and in Phyllanthus emblica.[2]
Punicafolin is an isomer of tellimagrandin II and nupharin A, but the hexahydroxydiphenoyl group is not attached to the same hydroxyl groups in the glucose molecule.
Punicafolin has been shown to have tumor suppressive effects in dogs.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G. I.; Nishioka, I. (1985). "Punicafolin, an ellagitannin from the leaves of Punica granatum". Phytochemistry. 24 (9): 2075–2078. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)83125-8.
- ^ Zhang, Y. J.; Abe, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yang, C. R.; Kouno, I. (2001). "Phyllanemblinins A-F, new ellagitannins from Phyllanthus emblica". Journal of Natural Products. 64 (12): 1527–1532. doi:10.1021/np010370g. PMID 11754604.
- ^ Tanimura S et al (2005) Suppression of tumor cell invasiveness by hydrolyzable tannins (plant polyphenols) via the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330(4):1306-1313
