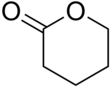
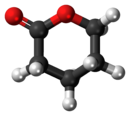
δ-Valerolactone
Appearance
(Redirected from Δ-valerolactone)
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxan-2-one | |||
| Other names
Penta-1,5-lactone
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.007 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties[2] | |||
| C5H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 100.117 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.079 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | −13 °C (9 °F; 260 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 230 to 260 °C (446 to 500 °F; 503 to 533 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 112 °C (234 °F; 385 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
δ-Valerolactone (delta-valerolactone) is a lactone used as a chemical intermediate in processes such as the production of polyesters.[3]
Natural occurrence
[edit]δ-Valerolactone can be found in Aspalathus linearis and Clerodendrum mandarinorum.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ delta-Valerolactone from BASF
- ^ delta-Valerolactone, Chemlink
- ^ Yang J, Jia L, Hao Q, et al. (2005). "New biodegradable amphiphilic block copolymers of epsilon-caprolactone and delta-valerolactone catalyzed by novel aluminum metal complexes. II. Micellization and solution to gel transition". Macromolecular Bioscience. 5 (9): 896–903. doi:10.1002/mabi.200500096. PMID 16134088.
- ^ "NP-MRD: Showing NP-Card for delta-valerolactone (NP0213348)". np-mrd.org. Retrieved 2024-02-17.