Shakya
Shakya Republic | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 7th century BCE–c. 5th century BCE | |||||||||
 Shakya among the Gaṇasaṅghas | |||||||||
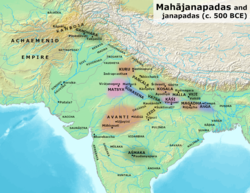 Shakya to the north of the Mahajanapadas in the post-Vedic period | |||||||||
| Status | Vassal state of Kosala | ||||||||
| Capital | Kapilavastu | ||||||||
| Common languages | Prakrits Munda languages[1] | ||||||||
| Religion | Sramana religions, Sun worship, tree worship, serpent worship | ||||||||
| Government | Aristocratic Republic | ||||||||
| Legislature | Sabhā | ||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||||
• Established | c. 7th century BCE | ||||||||
• Conquered by Viḍūḍabha of Kosala | c. 5th century BCE | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | India Nepal | ||||||||

Shakya (Pāḷi: Sakya; Sanskrit: शाक्य, romanized: Śākya) was an ancient clan of the northeastern region of South Asia, whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The Shakyas were organised into a gaṇasaṅgha (an aristocratic oligarchic republic), also known as the Shakya Republic.[2] The Shakyas were on the periphery, both geographically and culturally, of the eastern Indo-Gangetic Plain in the Greater Magadha cultural region.[1][3]
Location
[edit]
The Shakyas lived in the Terai – an area south of the foothills of the Himalayas and north of the Indo-Gangetic Plain with their neighbors to the west and south being the kingdom of Kosala, their neighbors to the east across the Rohni River being the related Koliya tribe, while on the northeast they bordered on the Mallakas of Kushinagar. To the north, the territory of the Shakyas stretched into the Himalayas until the forested regions of the mountains, which formed their northern border.[2]
The capital of the Shakyas was the city of Kapilavastu.[2][4]
Etymology
[edit]The name of the Shakyas is attested primarily in the Pali forms Sakya and Sakka, and the Sanskrit form Śākya.[5]
The Shakyas' name was derived from the Sanskrit root śak (शक्) (śaknoti (शक्नोति), more rarely śakyati (शक्यति) or śakyate (शक्यते)) meaning "to be able," "worthy," "possible," or "practicable."[2][6]
The name of the Shakyas was also derived from the name of the śaka or sāka tree,[7][6] which Bryan Levman has identified with either the teak or sāla tree,[6][1] which is ultimately related to word śākhā (शाखा), meaning 'branch,’[8] and was connected to the Shakyas' practice of worshipping the śaka or sāka tree.[1]
History
[edit]Origin
[edit]The Shakyas were an eastern sub-Himalayan ethnic group on the periphery, both geographically and culturally, of the eastern Gangetic plain in the Greater Magadha cultural region.[9][3] The Shakyas were of 'mixed origin' (saṃkīrṇa-yonayaḥ) of Indo-Aryan and Munda descent, with the former group forming a minority.[9] The Shakyas were closely related to their eastern neighbours, the Koliya tribe, with whom they intermarried.[10]
Alternative origin hypothesis
[edit]Scholars such as Michael Witzel and Christopher I. Beckwith have equated the Shakyas with Central Asian nomads who were called Scythians by the Greeks, Sakās by the Achaemenid Persians, and Śāka by the Indo-Aryans. These scholars have suggested that the people of the Buddha were Saka soldiers who arrived in South Asia in the army of Darius the Great during the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley, and saw in Scytho-Saka nomadism the origin of the wandering asceticism of the Buddha.[11][12]
Scholars criticize the Scythian hypothesis due to a lack of evidence, with Bryan Levman maintaining that the Shakyas were native to the north-east Gangetic plain and unrelated to the Iranic Sakas.[13]
Statehood
[edit]By the sixth century BCE, the Shakyas, the Koliyas, Moriyas, and Mallakas lived between the territories of the Kauśalyas to the west and the Licchavikas and Vaidehas to the east, thus separating the Vajjika League from the Kosala kingdom.[2] By that time, the Shakya republic had become a vassal state of the larger Kingdom of Kosala.[14][15]
During the fifth century itself, one of the members of the ruling aristocratic oligarchy of the Shakyas was Suddhodana. Suddhodana was married to the princess Māyā, who was the daughter of a Koliya noble, and the son of Suddhodana and Māyā was Siddhartha Gautama, the historical Buddha and founder of Buddhism.[2]
During the life of the Buddha, an armed feud opposed the Shakyas and the Koliyas concerning the waters of the river Rohiṇī, which formed the boundary between the two states and whose water was needed by both of them to irrigate their crops. The intervention of the Buddha finally put an end to these hostilities.[2]
After the death of the Buddha, the Shakyas claimed a share of his relics from the Mallakas of Kusinārā on the grounds that he had been a Shakya.[2]
Conquest by Kosala
[edit]Shortly after the Buddha's death, the Kauśalya king Viḍūḍabha, who had overthrown his father Pasenadi, invaded the Shakya and Koliya republics, seeking to conquer their territories because they had once been part of Kosala. Viḍūḍabha finally triumphed over the Shakyas and Koliyas and annexed their state after a long war with massive loss of lives on both sides. Details of this war were exaggerated by later Buddhist accounts, which claimed that Viḍūḍabha exterminated the Shakyas in retaliation for having given in marriage to his father the slave girl who became Viḍūḍabha's mother. In actuality, Viḍūḍabha's invasion of Shakya might instead have had similar motivations to the conquest of the Vajjika League by Viḍūḍabha's relative, the Māgadhī king Ajātasattu, who, because he was the son of a Vajjika princess, was therefore interested in the territory of his mother's homeland. The result of the Kauśalya invasion was that the Shakyas and Koliyas merely lost political importance after being annexed into Viḍūḍabha's kingdom. The Shakyas nevertheless soon disappeared as an ethnic group after their annexation, having become absorbed into the population of Kosala, with only a few displaced families maintaining the Shakya identity later. The Koliyas likewise disappeared as a polity and as a tribe soon after their annexation.[2][10]
The massive life losses incurred by Kosala during its conquest of Shakya and Koliya weakened it significantly enough that it was itself soon annexed by its eastern neighbour, the kingdom of Magadha, and its king Viḍūḍabha was defeated and killed by the Māgadhī king Ajātasattu.[2]
Legacy
[edit]

In Buddhism
[edit]The Buddha was given the epithet of the "Sage of the Shakyas," Sakka-muni in Pali and Śākya-muni in Sanskrit, by his followers.[17]
The functioning of the proceedings in the Trāyastriṃśa heaven ruled by Sakka, lord of the devas in Buddhist cosmology, are modelled on those of the Shakya santhāgāra or general assembly hall.[2]
Descent claims
[edit]Tharu people of Tarai region of India and Nepal claim descent from Sakya.[18] Significant population of Newars of Kathmandu valley in Nepal use the surname Shakya and also claim to be the descendants of the Shakya clan with titles such as Śākyavamsa (of the Shakya lineage) having been used in the past.[19]
According to Hmannan Yazawin, first published in 1823, the legendary king Abhiyaza, who founded the Tagaung Kingdom and the Burmese monarchy belonged to the same Shakya clan of the Buddha.[20] He migrated to present-day Burma after the annexation of the Shakya kingdom by Kosala. The earlier Burmese accounts stated that he was a descendant of Pyusawhti, son of a solar spirit and a dragon princess.[21]
Culture and society
[edit]Ethnicity
[edit]The Shakyas lived in what scholars presently call the Greater Magadha cultural area, which was located in the eastern Gangetic plain to the east of the confluence of the Gaṅgā and Yamunā rivers. Like the other eastern groups of the Greater Magadha region, the Shakyas were saṃkīrṇa-yonayaḥ ("of mixed origin"), and therefore did not subscribe to the caturvarṇa social organisation consisting of brāhmaṇas, khattiyas, vessas, and sudda. While non-Indo-Aryan indigenous clans were given the status of suddas, that is of slaves or servants, indigenous clans who collaborated with the Indo-Aryan clans were the status of khattiyas. The Buddhist suttas are ambiguous on the status of the Buddha, sometimes calling him a kshatriya, but mostly ignoring the varna system. Additionally, the populations of Greater Magadha did not subscribe to the supremacy of the brāhmaṇas of the peoples of Āryāvarta, and khattiyas were regarded as higher in the societies of Greater Magadha.[1]
Vedic literature therefore considered the populations of Greater Magadha as existing outside of the limits of Āryāvarta, with the Manusmṛiti grouping the Vaidehas, Māgadhīs, Licchavikas, and Mallakas, who were the neighbours of the Shakyas, as being "non-Aryan" and born from mixed caste marriages, and the Baudhāyana-Dharmaśāstras requiring visitors to these lands to perform purificatory sacrifices as expiation.[1]
This negative view of the peoples of the Greater Magadha region by the Vedic peoples extended to the Shakyas, as recorded in the Ambaṭṭha Sutta, according to which the brāhmaṇas described the Shakyas as "fierce, rough-spoken, touchy and violent," and accused them of not honouring, respecting, esteeming, revering or paying homage to the brāhmaṇas owing to their "menial origin."[1]
Language
[edit]The Shakyans were at least bilingual, under the linguistic influence of Munda languages, as attested by many of their villages having Mundari names, and the name of the founder of their clan, which has been recorded in the Sanskrit form Ikṣvāku and the Pali form Okkāka, being of Munda origin.[9]
Social organisation
[edit]Class system
[edit]The society of the Shakyas and Koliyas was a stratified one which did not subscribe to the caturvarṇa social organisation consisting of brāhmaṇas, khattiyas, vessas, and suddas, but instead consisted of an aristocratic class of khattiyas and a slave or servant class of suddas,[1] themselves comprising at least an aristocracy, as well as land-owners, attendants, labourers, and serfs.[2][10]
Landholders held the title of bhojakās, literally meaning "enjoyers (of the right to own land)," and used in the sense of "headmen."[2][10]
The lower classes of Shakya society consisted of servants, in Pāli called kammakaras (lit. 'labourers') and sevakas (lit. 'serfs'), who performed the labour in the farms.[1][10]
Administrative structure
[edit]The Sakyas were organised into a gaṇasaṅgha (an aristocratic oligarchic republic) similarly to the Licchavikas.[2][1]
The assembly
[edit]The heads of the Sakya khattiya clans of the Gotama gotta formed an Assembly, and they held the title of rājās. The position of rājā was hereditary, and after a rājā's death was passed to his eldest son, who while he was living held the title of uparājā ("Viceroy").[2][6]
The political system of the Sakyas was identical to that of the Koliyas, and like the Koliyas and the other gaṇasaṅghas, the Assembly met in a santhāgāra, the main of which was located at Kapilavatthu, although at least one other Sakya santhāgāra also existed at Cātuma. The judicial and legislative functions of the Assembly of the Sakyas were not distinctly separated, and it met to discuss important issues concerning public affairs, such as war, peace, and alliances. The Sakya Assembly deliberated on important issues, and it had a simple voting system through either raising hands or the use of wooden chips.[2]
The council
[edit]Similarly to the other gaṇasaṅghas, the Sakya Assembly met rarely and it instead had an inner and smaller Council which met more often to administer the republic in the name of the Assembly. The members of the council, titled amaccās, formed a college which was directly in charge of public affairs of the republic.[2]
The mahārājā (Consul)
[edit]The head of the Sakya republic was an elected chief, which was a position of first among equals similar to Roman consuls and Greek archons, and whose incumbent had the title of mahārājā. The mahārājā was in charge of administering the republic with the help of the council.[2][10]
Functioning of the assembly
[edit]When sessions of the Assembly were held, the rājās gathered in the santhāgāra; while four amaccās were posted in the four corners or sides of the hall so as to clearly and easily hear the speeches made by the rājās; and the consul rājā took his appointed seat and put forward the matters to be discussed once the Assembly was ready.[2]
During the session, the members of the Assembly expressed their views, which the four amaccās would record. The Assembly was then adjourned, after which the recorders compared their notes, and all the amaccās came back and waited for the recorders' decision.[2]
Lifestyle
[edit]Aristocratic marriage customs
[edit]Another reflection of non-Indo-Aryan cultural practices of the Shakyas was the practice of sibling marriages among their ruling clans, which was forbidden among Vaidika peoples, and was a practice of social demarcation and of maintaining power within a smaller sub-group of the Shakya clan, and was therefore not permitted among the lower classes of the Shakya.[1]
Religion
[edit]Since they lived in the Greater Magadha cultural area, the Shakyas followed non-Vedic religious customs which drastically differed from the Brahmanical tradition,[1] and even by the time of the Buddha, Brahmanism and the brāhmaṇas had not acquired religious or cultural preponderance in the Greater Magadha area to which Shakya belonged.[22]
It was in this non-Vedic cultural environment that Śramaṇa movements existed, with one of them, Buddhism, having been founded by the Shakya Siddhartha Gautama, the historical Buddha.[1]
Sun worship
[edit]The Shakyas worshipped the Sun-god, whom they considered their ancestor,[23] hence why the Shakya khattiya clan claimed to be of the Ādicca (Āditya in Sanskrit) gotta,[24][25] and of the Sūryavaṃśa ("Solar dynasty").[6]
Origin myth
[edit]The Shakya khattiya clan claimed descent from the Sun-god via his descendant, named Okkāka (in Pāli) and Ikṣvāku (in Sanskrit), and whose eight twin sons and daughters who were married to each other had founded the capital city of the Shakyas and were the tribe's ancestors. This was an origin myth of the ruling status of the khattiya families of the Shakya clan, who had the right to be represented in the santhāgāra, were often related to each other, and possessed adjacent areas of land, thus establishing kinship, which itself helped form rights of landownership, and, therefore, of political authority.[6]
This myth was also a foundation myth of the city which, as the residence of the ruling families of the clan, the city, which was the centre of political and economic activity, was associated with that clan's janapada (territory), and was equated with the whole janapada itself.[6]
The myth of the Shakyas' ancestors being four pairs of married twin siblings was a myth which traced the origins of the ruling Shakya families to a common ancestor, and was also a myth of an early human utopia where humans were born as couples.[6]
Tree worship
[edit]The important role of the Sāl tree in the life of the Buddha according to the Buddhist texts, as well as his representation as a Bodhi tree and his Enlightenment occurring under one such tree, suggest that the Shakyas practised tree worship, a custom likely derived from Munda religious customs of worshipping sacred groves, and the important role in their traditions of the Sāl tree, whose flowering marks the beginning of their New Year and Flower Feast festivals: the Santal tribe worship the Sāl tree and gather to make communal decisions under them Sāl trees.[1]
The importance of the tree spirits called yakkhas and yakkhīs in Pali (yakṣas and yakṣīs in Sanskrit) in early Buddhist texts is an attestation of the worship of these beings done at yakkha cetiyas. The worship of yakkhas and yakkhīs, which was of pre-Indo-Aryan autochthonous origin, was prevalent in the Greater Magadha region.[1]
Serpent worship
[edit]The nāga king Mucalinda, who in Buddhist mythology protected the Buddha during a storm under a mucalinda tree, was a both snake- and a tree-deity, thus alluding to the practice of serpent worship among the Shakyas, which originated from among the pre-Indo-Aryan Tibeto-Burman populations of northern South Asia.[1]
Funerary customs
[edit]The cremation rituals of the Shakyas which were performed for the funeral of the Buddha as described by Buddhist texts involved wrapping his body in 500 layers of cloth, placing it in an iron vat full of oil as a mark of honour, and then covering it with another iron pot before being cremated. These rites originated from the pre-Indo-Aryan autochthonous populations of the eastern Gangetic plains, as were the practices such as honouring the Buddha's body with singing, dancing, and music, as well as placing his bones in a golden urn, the veneration of these remains and their burial in a round stūpa which possessed a central mast, flags, pennants, and parasols at a public crossroads, which were rituals that were performed by the pre-Indo-Aryan populations for their greater rulers.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Levman 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Sharma 1968, p. 182-206.
- ^ a b Bronkhorst 2007, p. 6.
- ^ Trainor, K (2010). "Kapilavastu". In Keown, D; Prebish, CS (eds.). Encyclopedia of Buddhism. Milton Park, UK: Routledge. pp. 436–7. ISBN 978-0-415-55624-8.
- ^ Sharma 1968, pp. 182–206.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Thapar 2013, p. 392-399.
- ^ Fleet, J. F. (1906). "The Inscription on the Piprawa Vase". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. 38 (1): 149–180. doi:10.1017/S0035869X00034079. JSTOR 2521022. S2CID 161625116.
we find only a fanciful desire to account for the name Sakya by identifying it with the word sakya, śakya, in the sense of 'able, capable, smart.' But, looking below the surface, we find in the allusion to sākasaṇḍa, sākavanasaṇḍa, the grove of teak-trees, the real origin of the other name, Sākiya, Śākiya, Śākya.
- ^ Douglas Q., Adams; Mallory, J. P. (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. UK: Routledge. p. 208. ISBN 978-1-884-96498-5.
- ^ a b c Levman 2014: "The founder of the Sakya clan, King Ikṣvāku (Pāli: Okkāka) has a Munda name, suggesting that the Sakyas were at least bilingual (Kuiper 1991, 7; Mayrhofer 1992, vol. 1, 185). Many of the Sakya village names are believed to be non-IA in origin (Thomas 1960, 23), and the very word for town or city (nagara; cf. the Sakya village Nagakara, the locus of the Cūḷasuññata Sutta ) is of Dravidian stock (Mayrhofer 1963, vol. 2, 125)."
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"The Sakya clan derive their ancestry from King Ikṣvāku, whose name is of Austro-Asiatic Munda origin (see above, page 148). While the Sakyans' rough speech and Munda ancestors do not prove that they spoke a non-IA language, there is a lot of other evidence suggesting that they were indeed a separate ethnic (and probably linguistic) group."
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"Okkāka was the legendary progenitor of the Sakyas, and bears a name of Munda ancestry" - ^ a b c d e f Sharma 1968, p. 207-217.
- ^ Attwood, Jayarava (2012). "Possible Iranian Origins for the Śākyas and Aspects of Buddhism". Journal of the Oxford Centre For Buddhist Studies. 3: 47–69. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ^ Beckwith, Christopher I. (2015). Greek Buddha: Pyrrho's Encounter with Early Buddhism in Central Asia. Princeton, New Jersey, United States: Princeton University Press. pp. 1–21. ISBN 978-0-691-17632-1.
- ^ Levman 2014: "The evidence for this final wave is however, very slim and there is no evidence for it in the Vedic texts; for their western origin, Witzel relies on a reference in Pāṇini (4.2.131, madravṛjyoḥ) to the Vṛjjis in dual relation with the Madras who are from the northwest, and to the Mallas in the Jaiminīya Brāhamaṇa (§198) as arising from the dust of Rajasthan. Neither the Sakyas nor any of the other eastern tribes are mentioned, and of course there is no proof that any of these are Indo-Aryan groups. I view the Sakyas and the later Śakas as two separate groups, the former being aboriginal."
- ^ Walshe, Maurice (1995). The Long Discourses of the Buddha: A Translation of the Digha Nikaya (PDF). Wisdom Publications. p. 409. ISBN 0-86171-103-3.
- ^ Batchelor 2015, Chapter 2, Section 2, 7th paragraph.
- ^ Leoshko, Janice (2017). Sacred Traces: British Explorations of Buddhism in South Asia. Routledge. p. 64. ISBN 9781351550307.
- ^ Sharma 1968, p. 159-168.
- ^ Skar, H. O. (1995). "Myths of origin: the Janajati Movement, local traditions, nationalism and identities in Nepal" (PDF). Contributions to Nepalese Studies. 22 (1): 31–42.
- ^ Gellner, David (1989). "Buddhist Monks or Kinsmen of the Buddha? Reflections on the Titles Traditionally Used by Sakyas in the Kathmandu Valley" (PDF). Kailash – Journal of Himalayan Studies. 15: 5–20.
- ^ Hla Pe, U (1985). Burma: Literature, Historiography, Scholarship, Language, Life, and Buddhism. Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. p. 57. ISBN 978-9971-98-800-5.
- ^ Lieberman, Victor B. (2003). Strange Parallels: Southeast Asia in Global Context, c. 800–1830, volume 1, Integration on the Mainland. Cambridge University Press. p. 196. ISBN 978-0-521-80496-7.
- ^ Bronkhorst, Johannes (2011). Buddhism in the Shadow of Brahmanism. Leiden, Netherlands; Boston, United States: Brill. p. 1. ISBN 978-9-004-20140-8.
- ^ Batchelor 2015, p. 32-33.
- ^ Batchelor 2015, p. 36.
- ^ Nakamura, Hajime (2000). Gotama Buddha: A Biography Based on the Most Reliable Texts. Vol. 1. Tokyo, Japan: Kosei Publishing Company. p. 124. ISBN 978-4-333-01893-2.
Sources
[edit]- Batchelor, Stephen (2015). After Buddhism: Rethinking the Dharma for a Secular Age. New Haven, Connecticut, United States: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-21622-6.
- Bronkhorst, Johannes (2007). Greater Magadha, Studies in the culture of Early India. doi:10.1163/ej.9789004157194.i-416. ISBN 978-9-047-41965-5.
- Levman, Bryan G. (2014). "Cultural Remnants of the Indigenous Peoples in the Buddhist Scriptures". Buddhist Studies Review. 30 (2): 145–180. doi:10.1558/bsrv.v30i2.145. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- Sharma, J. P. (1968). Republics in Ancient India, C. 1500 B.C.-500 B.C. Leiden, Netherlands: E. J. Brill. ISBN 978-9-004-02015-3.
- Thapar, Romila (2013). The Past Before Us. Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-72651-2.


